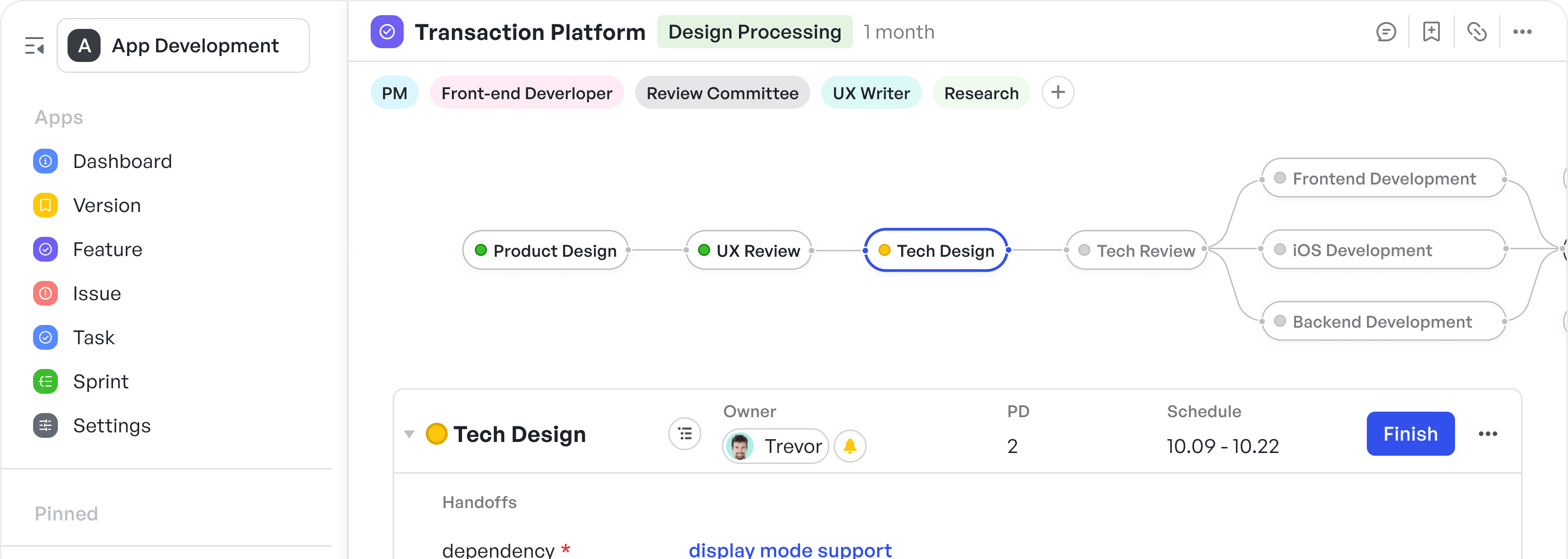
How to Implement Pair Programming in Manufacturing

Manufacturing companies rely heavily on precision, coordination, and repeatable processes. From automation systems to ERP integrations, software is increasingly becoming the nervous system of modern manufacturing. And as software plays a growing role, so does the importance of building it right. That’s where pair programming enters the scene.
Pair programming, a technique from Agile development where two engineers work together at one workstation, is gaining traction in manufacturing-driven tech teams. It enhances collaboration, reduces errors, and aligns development with real-world factory workflows.
In this post, we explore how pair programming fits manufacturing use cases, what benefits it brings to manufacturing-led software teams, and how to implement it effectively.
Why Pair Programming in Manufacturing Matters
In manufacturing environments, software systems are deeply embedded into production, logistics, compliance, and analytics. A small error in code can lead to disruptions, safety issues, or loss of throughput.
Unlike some applications where issues can be patched after deployment, software in manufacturing systems often interacts with physical equipment, leaving less room for mistakes. Pair programming helps reduce this risk in three specific ways:
- Fewer Bugs in Production: Two minds on the same task catch more issues early.
- Context Alignment: Developers better understand manufacturing workflows through constant discussion.
- Faster Knowledge Sharing: Engineers new to the domain get up to speed quickly by pairing with experienced peers.
For teams applying Lean principles, the Lean manufacturing project plan template can support how these iterative cycles are mapped into pairing sessions and retrospectives.
 Lean-aligned pairing and retrospectives planning
Lean-aligned pairing and retrospectives planning4 Use Cases Where Pair Programming in Manufacturing Works Best
Pair programming isn’t needed for every single ticket or bug fix. But in the manufacturing context, some tasks benefit significantly:
1. Building Real-Time Monitoring Tools
Writing software that pulls data from programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, or supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems requires high accuracy and deep domain understanding. Pairing reduces misalignment between what the system monitors and what operators need.
2. Configuring ERP and MES Integrations
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) or Manufacturing Execution Systems integrations can be complex. Pairing helps avoid configuration issues and data mapping errors, especially when working across vendor platforms.
3. Developing Predictive Maintenance Algorithms
Machine learning teams working on predictive maintenance can use pair programming to align data engineers and software developers. This improves model integration with production software.
In such scenarios, managing dependencies and timelines across roles becomes crucial. The production schedule management template is a great fit for teams who want to embed pair programming into larger feature releases tied to production uptime.
 Coordinate cross-role timelines and pair programming for production cycles
Coordinate cross-role timelines and pair programming for production cycles4. Compliance and Audit-Ready Code
Software systems that generate or store compliance data (e.g., ISO 9001 or FDA 21 CFR Part 11) benefit from peer-reviewed code via pairing. It reduces rework and supports audit-readiness.
You might be interested in: 👉Code review automation vs. peer review
How to Set Up Pair Programming in Manufacturing
If your manufacturing software team is new to pair programming, here are the key steps to get it working:
1. Start with a Pilot
Pick a high-priority feature or a difficult integration. Assign a senior and mid-level engineer to pair. Observe their output, collaboration, and feedback.
2. Define Roles and Rotate
In pair programming, one engineer is the "driver" (writing the code) and the other is the "observer" (reviewing in real time). Rotating roles help maintain energy and focus.
3. Use Visual Tools to Track Pairing Workflows
Templates that clarify tasks, owners, and timelines make pairing less chaotic. For example, the manufacturing project tracking dashboard template helps software teams within a factory ecosystem stay aligned across shifts and distributed units.
 Track tasks, owners, and timelines to support pairing across factory units
Track tasks, owners, and timelines to support pairing across factory unitsIf your team needs to maintain a clear map of who owns which code segment and what is being reviewed at each stage, the visual workflow feature in Meegle can provide a shared mental model, especially useful in multi-shift environments.
Advantages of Pair Programming in Manufacturing
Manufacturing-led tech teams that have adopted pair programming cite multiple advantages beyond fewer bugs:
- Better Communication with Ops Teams: Frequent pairing creates a culture of questioning, discussion, and clarity, benefiting how engineers talk to operations.
- Faster Onboarding of New Engineers: New hires learn systems and codebases faster when they pair.
- Higher Accuracy in Deployments: With fewer last-minute fixes, deployments are more stable and predictable.
- Shared Ownership: Less tribal knowledge and more collective confidence in what’s shipped.
The product lifecycle management template is especially effective when pairing needs to span across multiple stages, from planning to launch, enabling teams to track collaboration from feature design to delivery.
In an interview with Software Engineering Radio, Hans-Joachim Popp of the German Aerospace Center (DLR) described how their engineering teams implement a structured form of pair programming.
Junior developers are responsible for writing the code, while senior engineers provide continuous real-time review and critique. This practice is part of their broader commitment to code reliability, where they write approximately twelve lines of test code for every line of production code.
Although this approach yields just 0.6 lines of production code per hour, it reflects the level of precision required in mission-critical systems—an approach highly relevant to software teams in manufacturing environments.
Common Pitfalls of Pair Programming in Manufacturing
Not all pair programming attempts succeed. Here are challenges manufacturing teams face, and how to sidestep them:
Misaligned Skill Levels
Pairing a very senior developer with a new intern may result in an imbalance. Instead, pair people with 1–2 levels of experience difference.
Resistance to Pairing
Engineers used to solo work might push back. The best way to tackle this is through voluntary pilots and visible success stories.
Undefined Objectives
Pairing without clarity leads to confusion. Make sure every pairing session starts with a defined task and expected outcome.
Templates to Structure Pair Programming in Manufacturing
For manufacturing teams working on highly-regulated or multi-step processes, using templates to manage pairing assignments, deliverables, and timelines brings order to the process.
In addition to task-specific templates, the compliance management workflow template is a great resource when implementing pair programming on code related to regulation-heavy processes.
If you're also tracking code review sessions, consider adopting the pair programming session log template to build a history of progress, learning, and recurring issues across pairing cycles.
 Log code reviews and pairing sessions to track progress, learning, and patterns over time
Log code reviews and pairing sessions to track progress, learning, and patterns over timeThe Role of Tools in Pair Programming in Manufacturing
Pair programming isn’t just a people process. The right tools support:
- Real-time code sharing and commenting
- Task visibility and ownership tracking
- Workflow clarity across teams
Tools that support visual workflows are particularly effective in the manufacturing context because they mirror the process-centric thinking common in operations. It gives developers the same clarity operators get from floor plans or control panels.
If your team deals with tasks like shift-based planning or cross-functional development, the resource allocation template can help you visualize capacity and assign paired engineers based on skill availability.
 Visualize engineer capacity and assign pairs effectively with resource planning
Visualize engineer capacity and assign pairs effectively with resource planningBuild Accuracy and Alignment into Your Software Team
Manufacturing companies can no longer treat software development as a side function. It’s part of the core production environment. Pair programming adds a layer of safety, knowledge sharing, and alignment that solo work often misses.
If your manufacturing tech team is dealing with complex logic, critical integrations, or compliance requirements, pairing up might be your best productivity move yet.
Simplify dev teamwork in manufacturing with Meegle.
The world’s #1 visualized project management tool
Powered by the next gen visual workflow engineRead More
Check All BlogsStart creating impactful work today