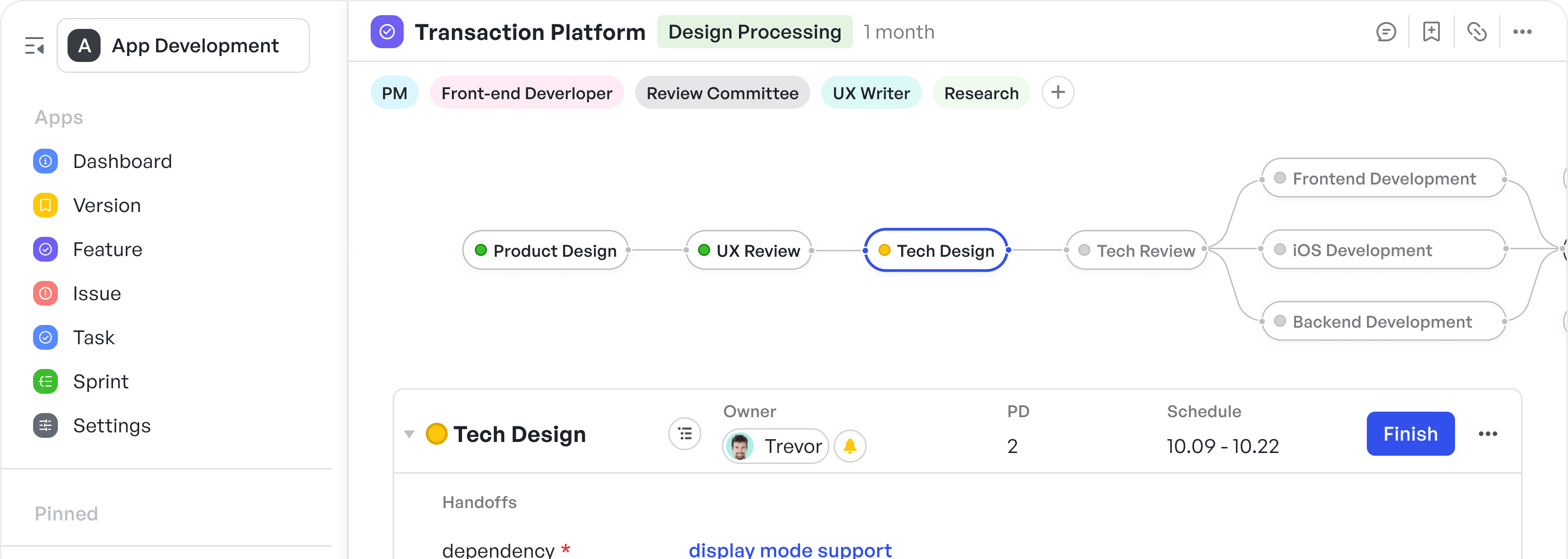
How To Implement Feature-Driven Development In Manufacturing

Manufacturing companies are under constant pressure to accelerate product delivery while maintaining strict quality and compliance standards. Managing complex processes that involve multiple teams and shifting priorities often exposes the limitations of conventional project management methods.
Feature-driven development (FDD), an Agile methodology focused on delivering discrete, valuable features, offers a practical framework to improve transparency and drive steady progress in manufacturing projects.
To fully appreciate the impact of feature-driven development in manufacturing, it is important to understand its core principles and how they address the specific challenges faced by manufacturing teams.
This article will explain the key steps and benefits of applying feature-driven development in a manufacturing context.
What Is Feature-Driven Development in Manufacturing?
Feature-driven development is an Agile methodology focused on delivering work as a series of well-defined, client-valued features. Unlike broader Agile frameworks that may focus on ceremonies or iterations, FDD centers on small, manageable pieces of functionality that collectively drive business value.
In manufacturing, this approach aligns well because product development naturally divides into features such as design specifications, component prototyping, testing cycles, and compliance checks. Having a structured plan for these features supports faster decision-making and improves coordination among diverse teams.
To help organize and track these stages, manufacturing teams can leverage the Product lifecycle management template. This template provides a clear visual framework to manage each feature’s progress, from initial design through testing phases to final compliance, enabling better transparency and smoother collaboration across departments.
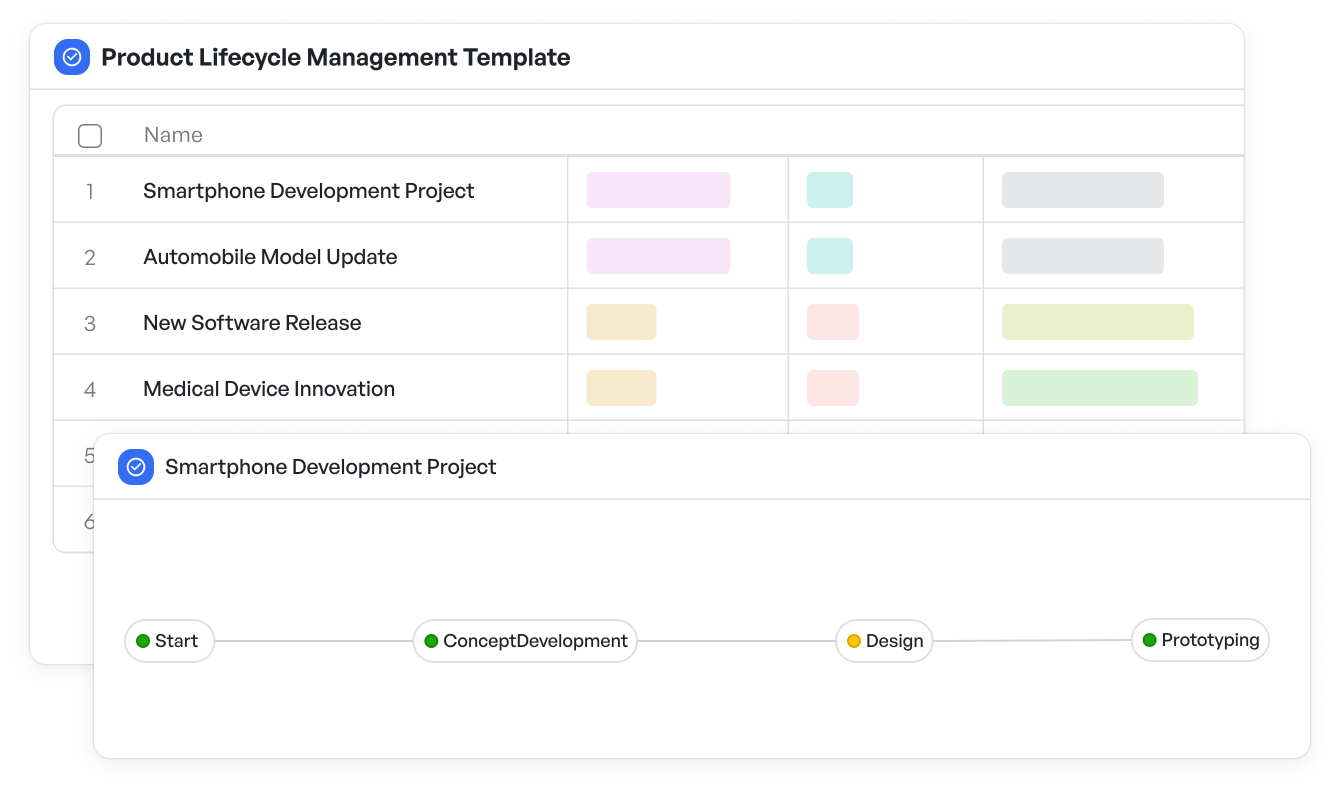 Visualize and manage feature stages with the product lifecycle management template
Visualize and manage feature stages with the product lifecycle management templateWhy Feature-Driven Development Matters for Manufacturing Teams
Manufacturing projects can be highly complex, involving multiple stakeholders such as engineers, quality assurance, supply chain, and compliance teams. Without clear visibility into progress and dependencies, teams risk delays and misalignment.
Feature-driven development addresses these challenges by:
- Providing transparency through feature-level tracking supported by tools like a project tracking dashboard template
- Breaking down complexity into measurable chunks
- Facilitating frequent progress reviews and course corrections
- Aligning work with regulatory and market-driven priorities
This structured yet flexible approach helps manufacturing teams keep projects on track while adapting to inevitable changes.
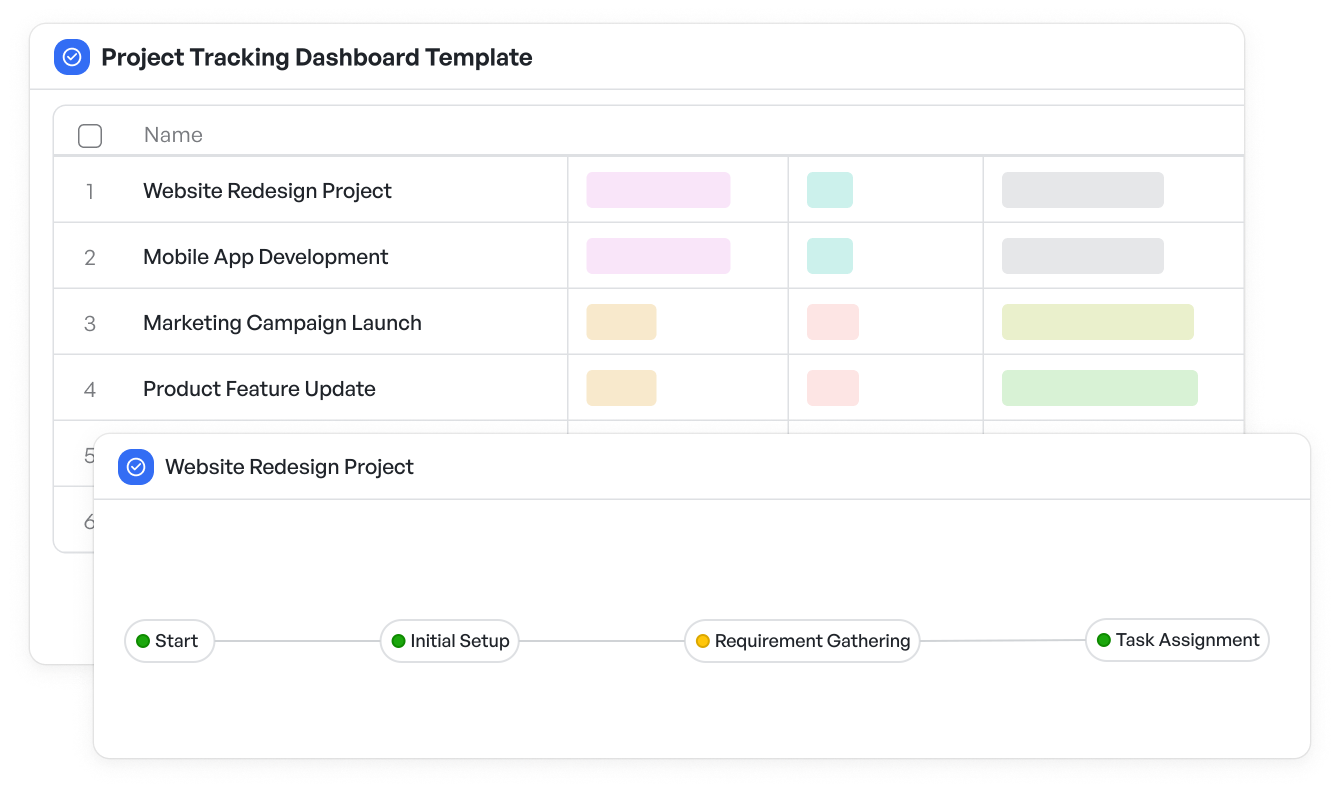 Track manufacturing features and progress with the project tracking dashboard template
Track manufacturing features and progress with the project tracking dashboard templateHow Feature-Driven Development Works in Manufacturing
Implementing FDD in manufacturing involves six key steps that focus the team’s efforts on delivering features with business value. Here’s an overview of how manufacturing organizations can apply FDD principles:
1. Develop an Overall Model
Begin by creating a high-level model of the manufacturing process or product development lifecycle. To visualize and analyze these workflows effectively, consider using a manufacturing process improvement template that helps establish a clear foundation for identifying features. This step identifies core components, workflows, and interactions, setting a foundation for feature identification.
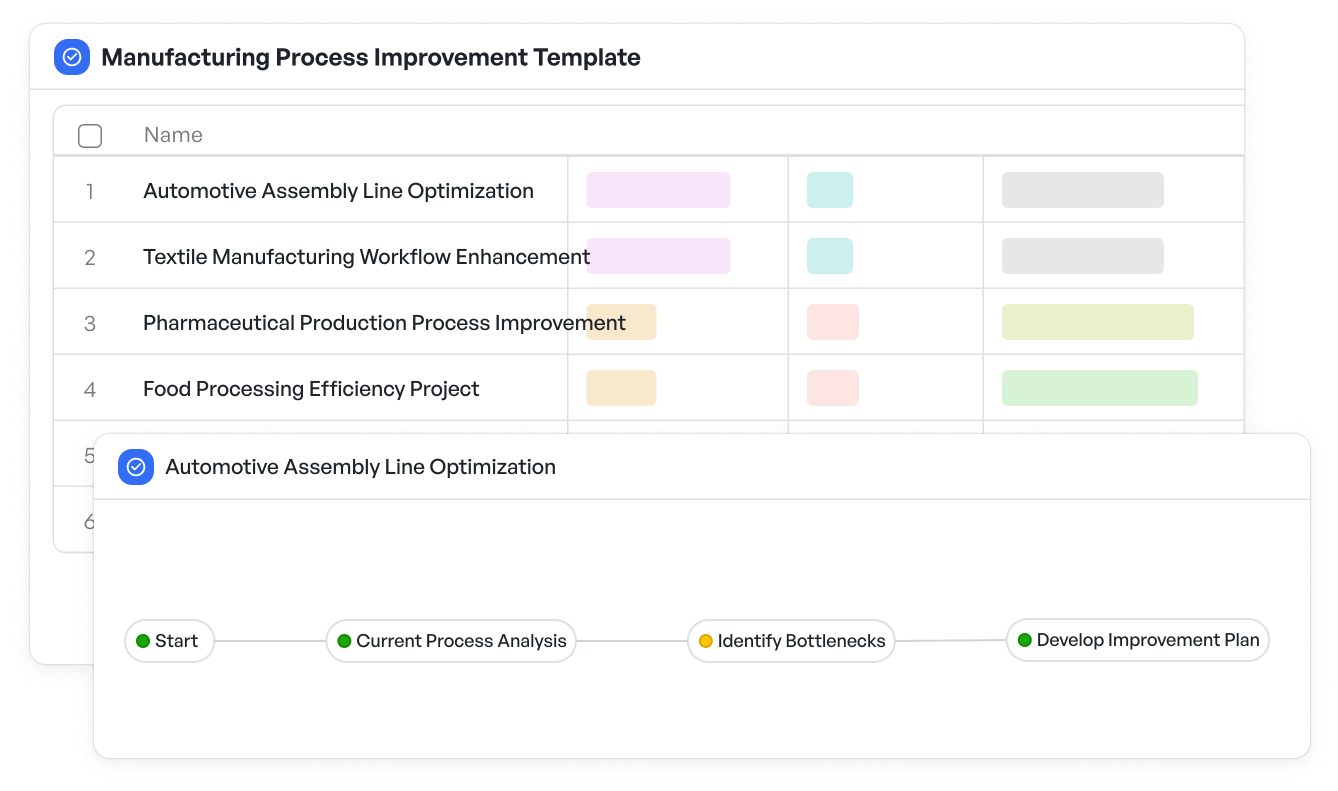 Streamline and visualize manufacturing workflows to identify continuous improvement opportunities
Streamline and visualize manufacturing workflows to identify continuous improvement opportunities2. Build a Feature List
Break down the model into a detailed list of features. For example, features might include “prototype chassis design,” “perform stress testing,” or “certify materials for compliance.” Each feature should be small enough to complete in a short cycle, allowing incremental delivery.
3. Plan by Feature
Prioritize features based on business impact, deadlines, and dependencies. Manufacturing teams might align these priorities with product launch schedules, supplier timelines, or regulatory audits.
Align your planning with production schedules and supplier timelines using a capacity planning template to allocate resources efficiently and avoid bottlenecks.
 Optimize resource allocation for smooth production flow
Optimize resource allocation for smooth production flow4. Design by Feature
Develop detailed designs or plans for each feature, specifying requirements, resources, and expected outcomes. This could involve CAD models, testing protocols, or documentation for certification.
5. Build by Feature
Carry out development, testing, and validation iteratively for each feature, fostering continuous feedback and reducing costly errors. Managing these quality checks becomes easier with a quality control workflow template.
 Streamline testing and validation for consistent quality
Streamline testing and validation for consistent quality6. Regular Progress Reporting
Track feature completion and progress through visual workflows or dashboards. Clear visibility helps teams stay aligned on timelines and resource allocation.
Enhancing Feature-Driven Development in Manufacturing with Visual Workflows
A critical element of effective Feature-Driven Development is visualizing workflows and project progress. Manufacturing projects involve numerous moving parts and interdependencies. Visual workflows provide every team member with a clear picture of ongoing tasks, responsibilities, and timelines.
Using visual workflow tools allows manufacturing teams to:
- Understand the status of each feature at a glance
- Identify bottlenecks early
- Coordinate efforts across departments
- Track collaboration and handoffs smoothly
This clarity leads to better decisions and on-time delivery.
 Workflow visualization in Meegle
Workflow visualization in MeegleChallenges Faced by Manufacturing Teams and How Feature-Driven Development Addresses Them
Manufacturing projects encounter several specific pain points. Some of them are:
- Complex coordination across disciplines: Engineering, supply, and quality teams often operate in silos, causing delays and miscommunication. FDD encourages incremental progress and better cross-team communication. Using a project tracking dashboard template can help visualize who’s responsible for each feature and track progress transparently across teams.
- Regulatory and compliance demands: Managing compliance in stages reduces risk and simplifies audits. A compliance management workflow aligns feature deliveries with regulatory requirements, helping teams maintain quality and meet standards efficiently.
 Compliance management workflow template
Compliance management workflow template- Time-to-market pressure: Focusing on high-priority features allows manufacturing teams to accelerate product readiness. Ensuring capacity planning helps allocate resources optimally to critical features, avoiding bottlenecks and providing faster delivery.
- Changing requirements: The Agile nature of FDD allows adaptation to design changes or supplier delays without disrupting overall progress.
By focusing on features, manufacturing teams can navigate these complexities with more confidence.
Integrating Feature-Driven Development with Manufacturing Software Tools
Manufacturing teams rely heavily on software tools for design, collaboration, and process management. Effective FDD implementation benefits from tools that support visual workflows, feature tracking, and flexible customization.
Many teams find that existing tools either handle complex projects poorly or are difficult to learn. A tool that strikes a balance—being both powerful and user-friendly—can significantly ease adoption.
Drive Manufacturing Success with Structured Agile Focus
Feature-driven development equips manufacturing teams with a clear, actionable approach to managing complex projects. By focusing on delivering measurable features in well-defined cycles, teams gain better visibility, improve collaboration, and adapt swiftly to change. This leads to faster product delivery, improved quality, and enhanced compliance management.
To support this approach, look for project management tools that offer flexible visual workflows tailored to your manufacturing processes. With the right system in place, manufacturing leaders can confidently meet deadlines, align teams, and deliver customer value.
Try Meegle and bring clarity, speed, and structure to every feature in your manufacturing process.
The world’s #1 visualized project management tool
Powered by the next gen visual workflow engineRead More
Check All BlogsStart creating impactful work today