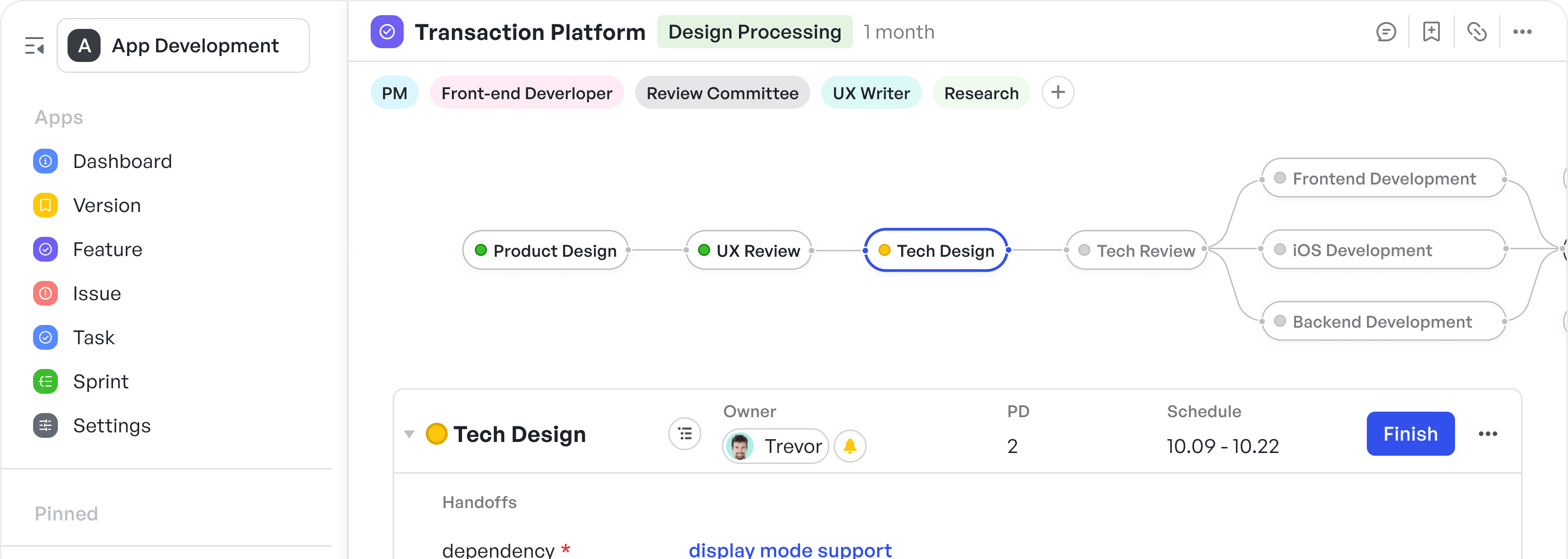
How To Implement Agile Modeling In Manufacturing

Agile methodologies are often associated with software development, but their adaptability makes them increasingly relevant for manufacturing operations. From automotive production lines to electronics assembly units, manufacturing leaders are discovering how Agile modeling can improve process visibility, reduce inefficiencies, and support collaboration across departments.
This article explores how Agile modeling is applied in manufacturing, the benefits it offers, and the practical steps to integrate it into complex, large-scale operations.
Why Agile Modeling in Manufacturing Matters
Manufacturing organizations face constant pressure to reduce lead times, optimize resources, and increase product quality. Traditional process modeling often falls short due to rigid structures and limited collaboration tools. Agile modeling provides a more flexible and iterative approach.
Agile modeling in manufacturing involves:
- Building lightweight, iterative process representations
- Continuously updating workflows as new insights or changes arise
- Visualizing current and future states for quick decision-making
Instead of creating overly detailed documentation upfront, teams iterate and adapt models in real time, making Agile particularly suited to dynamic production environments.
To effectively manage capacity adjustments and resource allocation while modeling workflows, teams can leverage the capacity planning template designed specifically for manufacturing needs.
 Agile modeling combined with tailored templates helps teams balance adaptability with precise resource management
Agile modeling combined with tailored templates helps teams balance adaptability with precise resource managementBenefits of Agile Modeling in Manufacturing Teams
Before diving into implementation, it’s useful to understand the specific gains manufacturing teams can expect:
1. Faster process adjustments
Teams can adjust workflows with less friction, allowing faster responses to equipment issues, supplier changes, maintenance management, or new regulations.
2. Enhanced cross-functional collaboration
Visual workflows help production, quality control, and procurement teams align their tasks and timelines without miscommunication.
3. Reduction in downtime and rework
Clear task ownership and visibility into interdependencies reduce delays and prevent costly errors during handoffs.
4. Improved traceability and compliance
By iterating on models and logging changes, manufacturing firms can maintain compliance while remaining flexible.
Visualizing ongoing production and project status with the project tracking dashboard template can help teams monitor progress and reduce downtime.
 Visualize project progress and keep manufacturing teams aligned in real time
Visualize project progress and keep manufacturing teams aligned in real time4 Core Principles of Agile Modeling in Manufacturing
To apply Agile modeling effectively in manufacturing environments, operations leaders and project managers should follow a few essential principles.
1. Model incrementally and iteratively
Start with just-enough detail. Use each production cycle to validate and expand your process models. Avoid overengineering workflows that may change soon.
2. Collaborate with diverse roles
Involve shop floor managers, engineers, and quality assurance in modeling. Use visual formats such as charts, graphs, and interactive dashboards that make complex information easier to understand and update collaboratively.
3. Prioritize real-time visualization
Use visual tools to represent workflow states: what has been done, what is in progress, and what is blocked. This enables quicker interventions and more accurate forecasting.
4. Incorporate feedback from real scenarios
Review workflows after each sprint or batch run. Use team feedback to refine the process continuously.
Incorporating structured processes with a quality control workflow template ensures collaboration between production and QA teams while adapting quality checkpoints.
 Ensure consistent product quality and streamline inspection processes with the quality control workflow template
Ensure consistent product quality and streamline inspection processes with the quality control workflow templateHow to Apply Agile Modeling in Manufacturing Projects in 5 Easy Steps
Implementing Agile modeling in manufacturing doesn’t require an overhaul. Here’s a practical path to follow.
Step 1: Define manufacturing workflows
Start by identifying key workflows such as production scheduling, quality checks, and material handling. Create simple initial models for these workflows.
Step 2: Introduce visual modeling tools
Use tools that support collaborative, visual modeling of workflows. These allow stakeholders to quickly understand and edit process flows.
Step 3: Conduct modeling sprints
Schedule short cycles where teams iterate on process models based on real-time performance and new requirements.
Step 4: Align with compliance needs
Model documentation updates should include revision logs and compliance tags where required, especially in regulated industries like automotive or pharma manufacturing.
Step 5: Monitor and adapt
Track how modeling affects production metrics, such as throughput, defect rates, or lead time, and evolve your modeling approach accordingly.
Tools like the compliance management workflow template help manufacturing teams keep up-to-date with regulatory documentation and audit readiness while iterating on processes.
 Audit-ready compliance with streamlined documentation using the compliance management workflow template
Audit-ready compliance with streamlined documentation using the compliance management workflow templateUse Cases of Agile Modeling in Manufacturing
Agile modeling supports a wide variety of scenarios in manufacturing. Some of the most impactful include:
1. New product introduction (NPI)
Use Agile workflows to coordinate between R&D, procurement, and production planning. This helps reduce launch delays and quality issues.
2. Quality control workflows
Model inspection checkpoints and feedback loops that adapt based on defect trends or regulatory changes.
3. Maintenance scheduling
Integrate real-time equipment data into Agile workflows to prioritize and sequence maintenance tasks more efficiently.
4. Supplier management
Collaborate with vendors on just-in-time manufacturing and delivery, shared inventories, or flexible restocking through a visual workflow.
For maintenance and equipment uptime, the equipment maintenance schedule template can organize task sequencing and prioritize urgent repairs.
 Optimize uptime and prioritize maintenance with the equipment maintenance schedule template
Optimize uptime and prioritize maintenance with the equipment maintenance schedule templateTemplates for Agile Modeling in Manufacturing Scenarios
Templates can speed up adoption by giving teams a head start on building workflows.
If you're modeling a sprint planning calendar for factory upgrades, or setting up a maintenance workflow tracker, starting with a pre-built agile sprint planning calendar can help teams align faster. This template offers a visual timeline to assign roles, track dependencies, and model sprints tailored to manufacturing cycles.
 Templates available for manufacturing in Meegle
Templates available for manufacturing in MeegleUnlocking Value with Agile Modeling in Manufacturing
Securing buy-in from manufacturing leaders is essential for Agile modeling to deliver real impact. Highlighting how Agile complements established methodologies like Lean and Six Sigma, sharing early wins through visual metrics, and emphasizing faster adaptation helps build support and momentum.
As Industry 4.0 and smart factory technologies evolve, Agile modeling will play a vital role in enabling manufacturers to model, test, and optimize both digital and physical processes with greater clarity and collaboration. For mid-market and enterprise operations, adopting Agile is the key to moving beyond chasing improvements to sustaining lasting operational excellence.
Modern manufacturing demands flexibility, visibility, and speed, values that Agile modeling and visual workflows provide when applied thoughtfully.
Build your workflow today!
The world’s #1 visualized project management tool
Powered by the next gen visual workflow engineRead More
Check All BlogsStart creating impactful work today