What Are Project Phases? How Many Do We Have?

Ask three project managers (PMs) how many phases a project has, and you'll likely get three different answers. Some say four, others say five, and a few break it down into seven. So, which is it?
The most commonly used breakdown is five phases: Initiation, Planning, Execution, Monitoring and Controlling, and Closure. But the uncertainty doesn't stop there.
Some PMs, like Dokuzetsuko, confuse project phases with project processes.
 Are project phases processes (Sources: Reddit)
Are project phases processes (Sources: Reddit)Others, like Heylauu, wonder which phase deserves the most attention.
 What project phase is most important (Source: Reddit)
What project phase is most important (Source: Reddit)Here's a quick answer for all: project phases and processes are different, and no single phase is more important than the others.
Each phase plays a specific role in guiding a project from concept to completion. In this article, we'll walk you through each phase, explain what it involves, and show why skipping any could throw your project off balance.
What are the phases of project management?
To understand project phases, it helps to view them through the lens of the project life cycle:
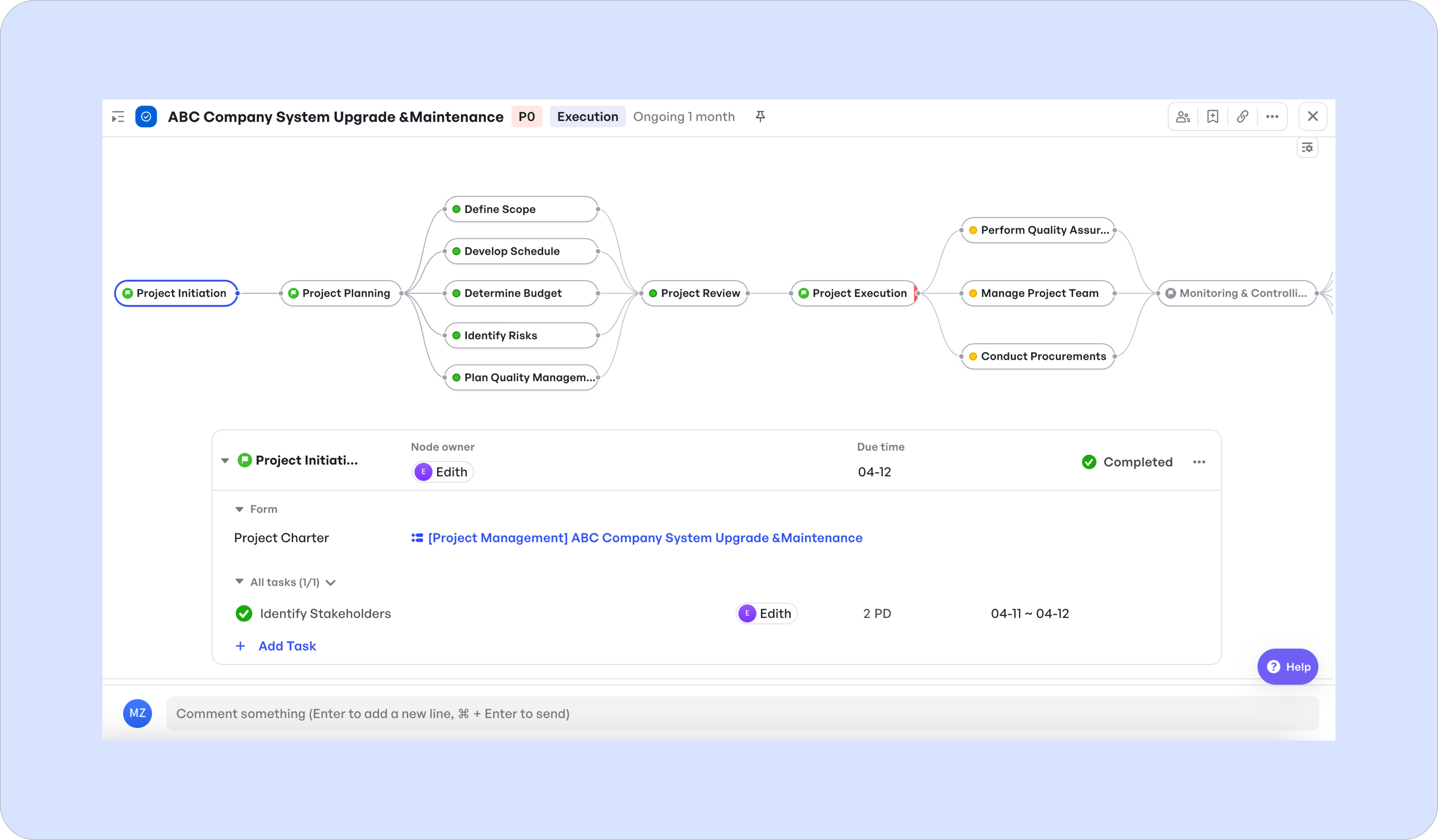 Project life cycle
Project life cycle- No project is completed all at once—teams tackle it in manageable parts.
- These parts, from Initiation through Planning to Closure, are known as phases.
- Each phase has distinct tasks, often handled by dedicated teams.
- Together, these phases make up what's called the project life cycle.
Later in this article, we'll explore how phases, tasks, and teams come together to shape the complete project life cycle.
So, what are project phases?
They're the sequential, manageable units of a project life cycle that give teams better control and visibility over the entire process.
How many phases are there?
| Model | Phases Included | When/Why Applicable |
|---|---|---|
| Model 1: 4 Phases | Initiation, Planning, Execution, and Closure | Best for smaller projects or when teams prefer a simple, high-level approach. Useful in academic settings or lightweight project environments. |
| Model 2: 5 Phases | Initiation, Planning, Execution, Monitoring and Controlling, and Closure | Most widely used in professional and corporate settings. Ideal for projects needing continuous oversight and formal project management standards. |
| Model 3: 7 Phases | Intake, Initiation, Planning, Product Selection, Execution, Monitoring and Controlling, and Closure | Suitable for complex IT or technology projects where early intake, procurement decisions, and ongoing monitoring are critical to success. |
The answer depends on who you ask. There are three commonly accepted models, and while all three are in use, the five-phase model by PMBOK® is more popular in professional settings.
Model 1: Four phases
This model is based on the book Project Management by Adrienne Watt (2nd Edition). Here, the cycle includes:
- Initiation
- Planning
- Execution
- Closure
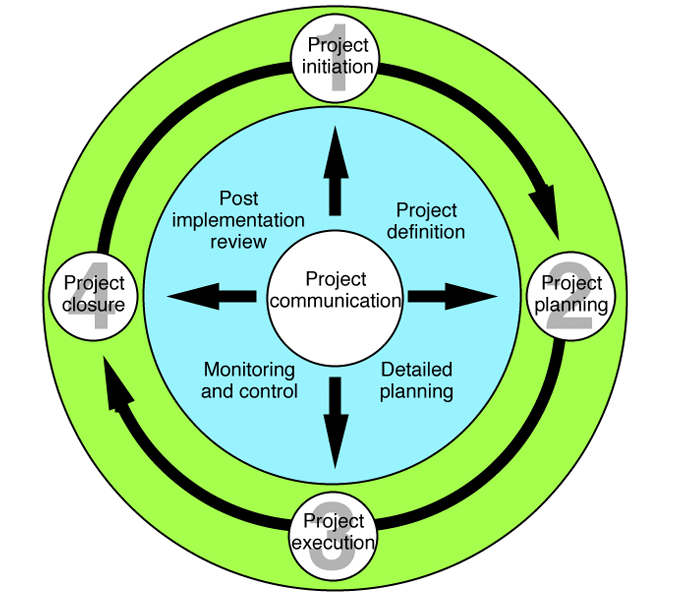 The four phases of project management (Source: Adrienne Watt's book)
The four phases of project management (Source: Adrienne Watt's book)Model 2: Five phases
Grounded in the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK®), this is the most widely used classification. Here, there's a fifth phase, Monitoring and Controlling:
- Initiation
- Planning
- Execution
- Monitoring and Controlling
- Closure
Related article for in-depth guide:👉 What is Project Management? The Complete Guide
Model 3: Seven phases
In some organizations, the project life cycle is broken down even further into seven detailed phases for better management and oversight.
- Intake
- Initiation
- Planning
- Product Selection
- Execution
- Monitoring and Controling
- Closure
For instance, organizations using Capgemini's Software Development Methodology (SDM) follow seven phases, including Information Planning, Definition Study, and Basic Design.
Similarly the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC), a well-known framework in software engineering, also follows a seven-phase model.
There's one issue, however. Project processes (process groups) also have Initiation, Planning, Execution, Monitoring, and Closure.
Do project phases mean the same as process groups?
Not quite. While project phases and process groups often share similar names—like Initiation, Planning, Execution, and Closure—they refer to different things.
- Phases are time-bound stages of a project, each with defined objectives and deliverables.
- Process groups are recurring activities throughout the project, regardless of the phase.
For example, during the Execution phase of a product build, you might still be:
- Monitoring deliverables
- Controlling quality
- Planning the next sprint
So, just as phases form the structure of the project life cycle, process groups are the core activities that span across these phases, often overlapping at various stages.
5 phases of project management
For this section, we'll use the 5-phase classification. Whether you're managing enterprise-scale projects or sprint-based initiatives, breaking work into 5 clear phases helps simplify complexity.
Moreover, Meegle offers a dedicated project life cycle template that supports each phase seamlessly—helping your team stay organized, accountable, and focused from start to finish.
TL;DR:
| Phase | Summary of Tasks | How Meegle Helps |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Initiation | Define project goals, identify stakeholders, gather initial requirements, align expectations, assess feasibility, and draft project charter | Meegle’s visualized workflows map stakeholder inputs and approval checkpoints, ensuring clarity and accountability from the start. Reduces miscommunication and approval delays. |
| 2. Planning | Break down work into tasks (WBS), set scope, assign responsibilities, build timeline, allocate resources, define dependencies, and set milestones | Meegle offers Gantt Charts, member schedules, and dependency mapping to build realistic, coordinated plans that prevent resource clashes or scheduling gaps. |
| 3. Execution | Assign tasks, manage deliverables, coordinate across teams, update timelines, ensure alignment with objectives | Node-driven workflows automate task handoffs between departments (e.g., marketing → dev), while integrated communication tools streamline feedback and cross-functional work. |
| 4. Monitoring | Track KPIs, monitor progress, manage risks, reassign tasks, address blockers, and report status to stakeholders | Real-time dashboards detect bottlenecks early. Custom alerts notify managers when progress stalls or critical metrics drop, helping teams stay on track. |
| 5. Closure | Finalize deliverables, conduct reviews, capture learnings, gain approvals, archive documents, and transition ownership where needed | Meegle uses charts and progress tracking to support project retrospectives and visualize performance. All documentation remains centralized for easy access and reuse. |
Phase 1: Initiation
The Initiation phase formally kicks off the project. It is where vetted ideas become approved initiatives with a clearly defined why, what, and who.
This phase is critical for securing leadership buy-in and laying the groundwork for feasibility and direction.
What's the goal of this phase?
To define the high-level scope, confirm project objectives, and align all stakeholders with expectations, budget, and success criteria.
What happens during Initiation?
Key tasks in this phase include:
- Assigning a project manager – Usually handled by the sponsor or senior leadership, this ensures someone owns the process from here forward.
- Writing a project charter – Typically done by the project manager or PMO, this document outlines the purpose, goals, scope, and stakeholders.
- Identifying risks and constraints – Conducted collaboratively by the project manager and key stakeholders to flag potential blockers and align on limitations early. This step differs from the risk identification process in the planning phase, which focuses on evaluating risks in more detail and developing mitigation strategies.
The primary players in Initiation are the project sponsor, key stakeholders, and the project manager. Together, they shape a shared understanding of success metrics and what it will take to get there.
Related read:👉15 Key Project Management Roles and Responsibilities
How does Meegle help?
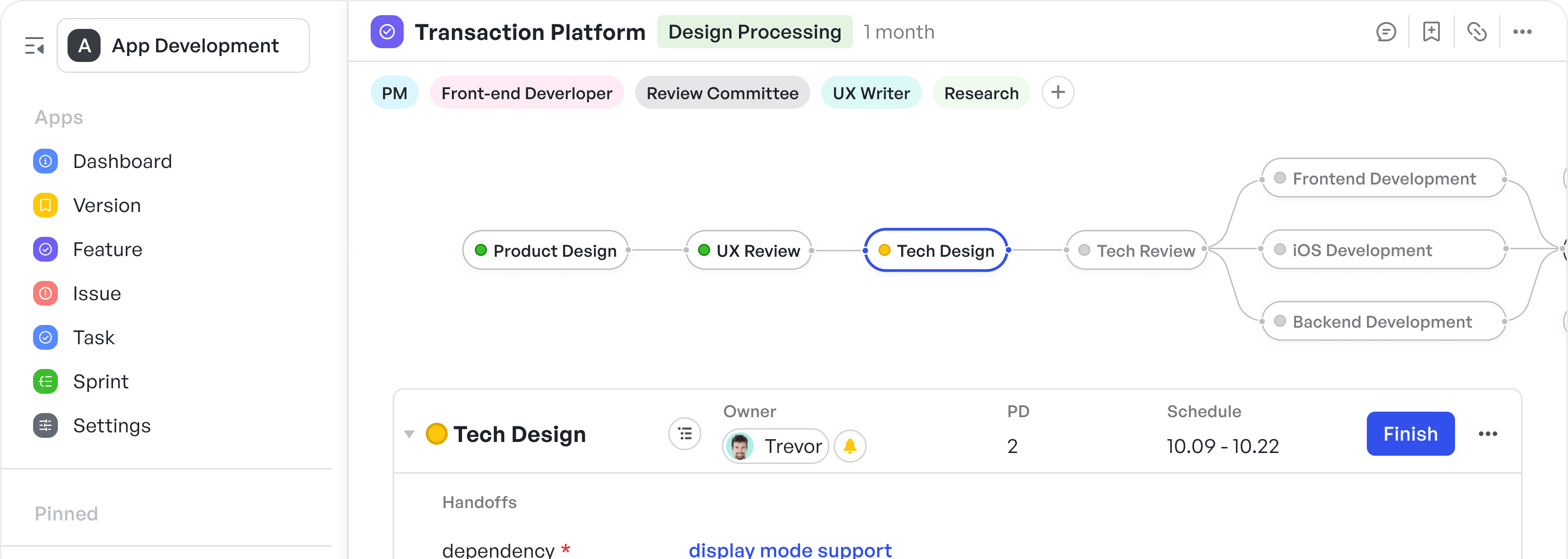
Meegle makes this phase actionable through node-driven visual workflows—interactive maps where each node represents a task, decision point, or stakeholder action.
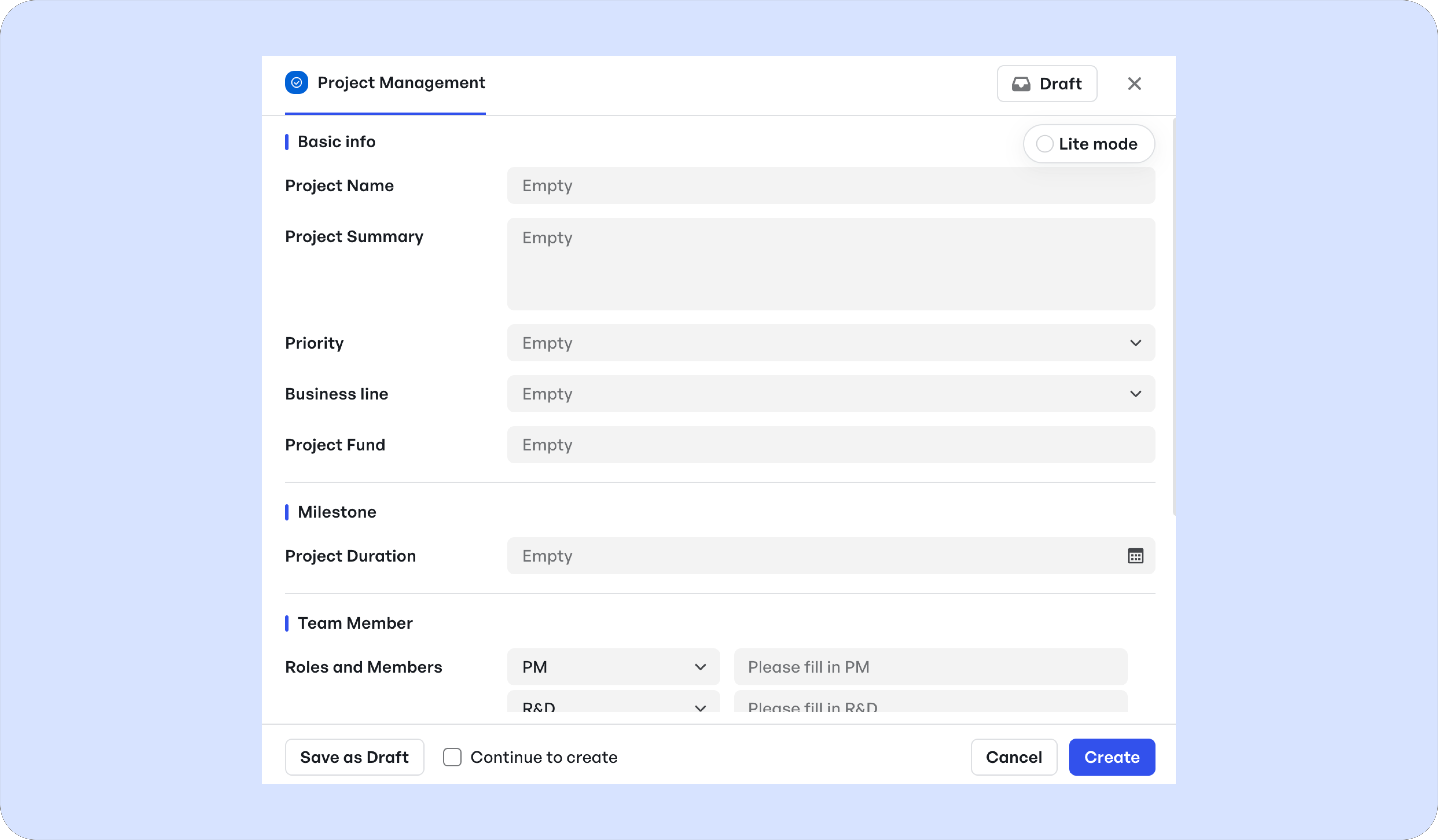 New project setup in Meegle
New project setup in Meegle- Role-based permissions: The visual workflow setup allows sponsors or senior leadership to assign a project manager as the "node owner" at the start of a workflow. This action makes the PM the centralized point of accountability, visible to all contributors. Assignments are time-stamped and tracked, ensuring clear ownership from the moment a project enters initiation.
 Node owner (PM), project charter, stakeholders added in Project Initiation phase in Meegle
Node owner (PM), project charter, stakeholders added in Project Initiation phase in Meegle- Project charter: The project manager can draft the charter within a shared space (integration with Lark docs comes in handy here), tag stakeholders for input, and track every comment or revision. Additionally, files can be uploaded for easy reference.
 Uploading files using Form tabs
Uploading files using Form tabsOnce a draft is created, workflow triggers move to a review node where key stakeholder or PMO can approve or suggest changes before the charter is finalized.
 Stakeholder input in initiation phase
Stakeholder input in initiation phasePhase 2: Planning
The Planning phase is where strategy turns into an actionable roadmap. It follows Initiation and is arguably the most critical phase for setting your project up for success.
What's the goal of this phase?
To simplify the project into manageable tasks with timelines, resource allocations, dependencies, and risk management strategies.
What happens during Planning?
This phase transforms the project vision into a detailed execution plan. Common tasks include:
- Defining the project scope in detail
- Creating work breakdown structures (WBS)
- Building project schedules and timelines
- Allocating resources across teams
- Setting milestones and deliverables
- Identifying risks and developing mitigation plans
- Developing a stakeholder communication plan
This phase is also where tools like Gantt Charts, calendars, and collaboration frameworks come into play.
Project managers lead this phase, working closely with team leads, operations, and finance to align on feasibility, costs, and capacity. Together, they build the blueprint for Execution to prevent scope creep, delays, or burnout.
Suggested Read:��Project Management Goals: 10 Examples
How does Meegle help?
In Meegle:
- PMs can add project scope details as text descriptions within the Planning workflow's node. Teams can upload project requirement documents or scope outlines, keeping everything centralized and editable in one place.
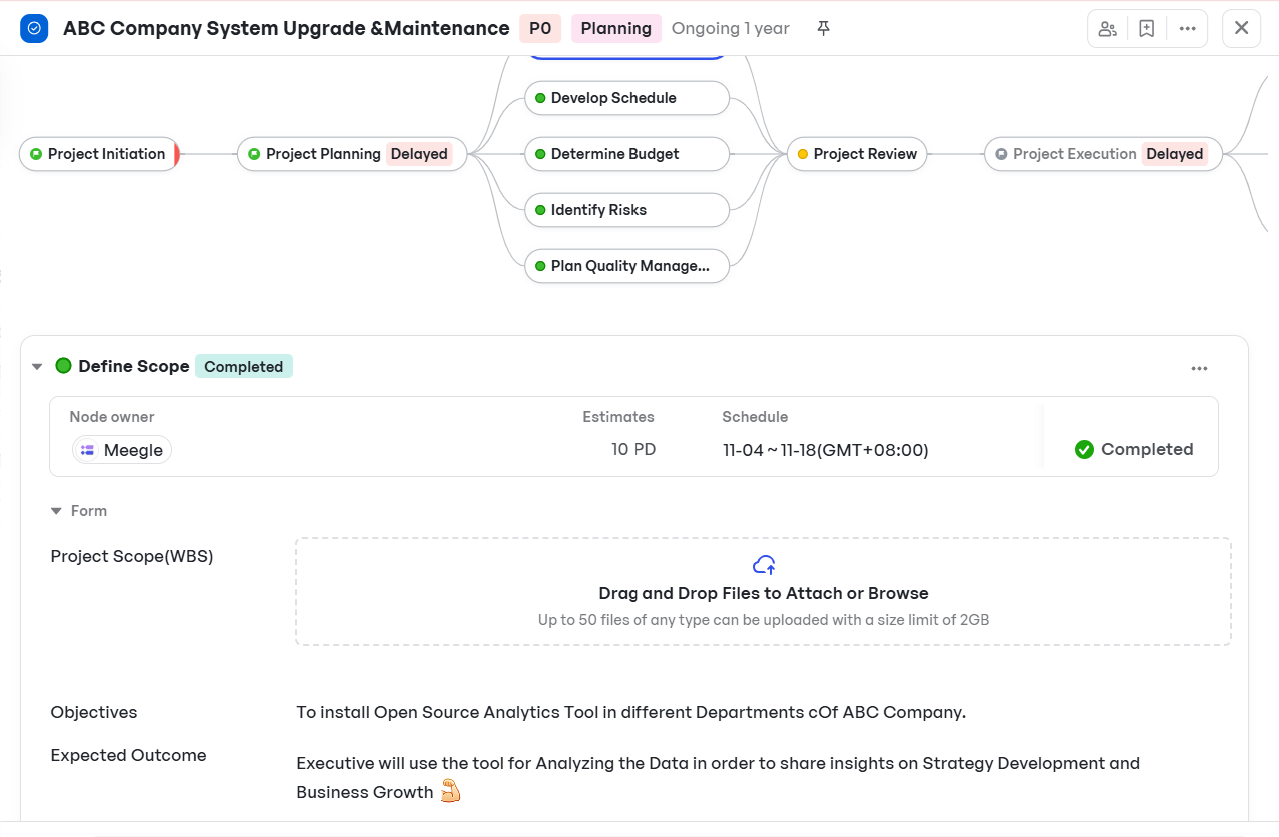 Uploading scope details on Meegle
Uploading scope details on Meegle- Meegle's node-driven workflows naturally act as a visual WBS. Each node can represent a key task or deliverable, broken down further into subtasks.
- Teams can assign owners, due dates, and attachments to each node, making it function like an interactive WBS layer. They can also use Meegle's Gantt Charts to visualize task durations, dependencies, and deadlines — adjusting timelines, aligning parallel workstreams, and updating progress in real time.
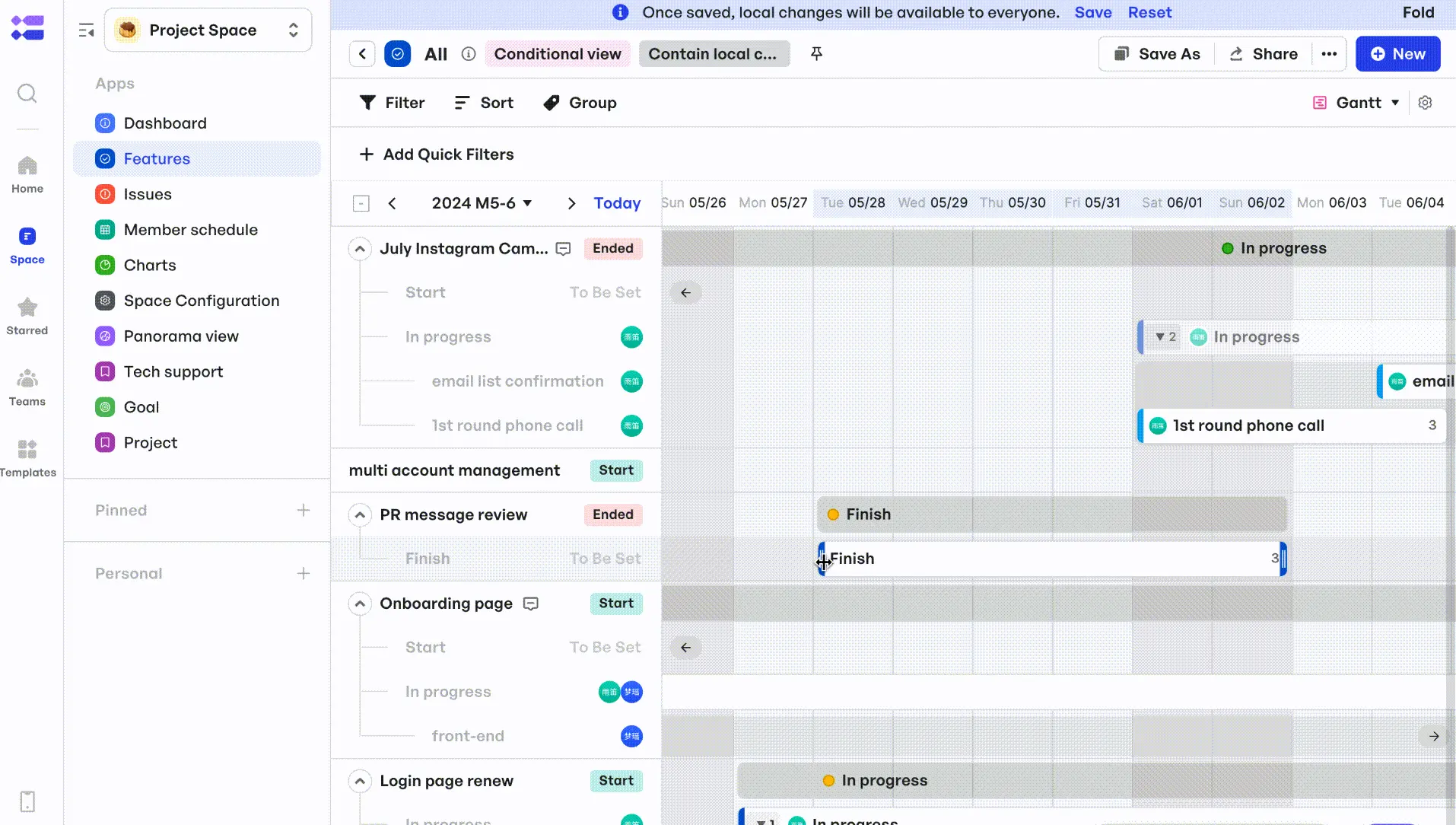 View project timelines at a glance
View project timelines at a glance- The Member Schedule feature displays team availability, workload, and conflicts, helping PMs make informed resourcing decisions. Teams can view who's overbooked, reassign tasks, or split responsibilities to avoid bottlenecks.
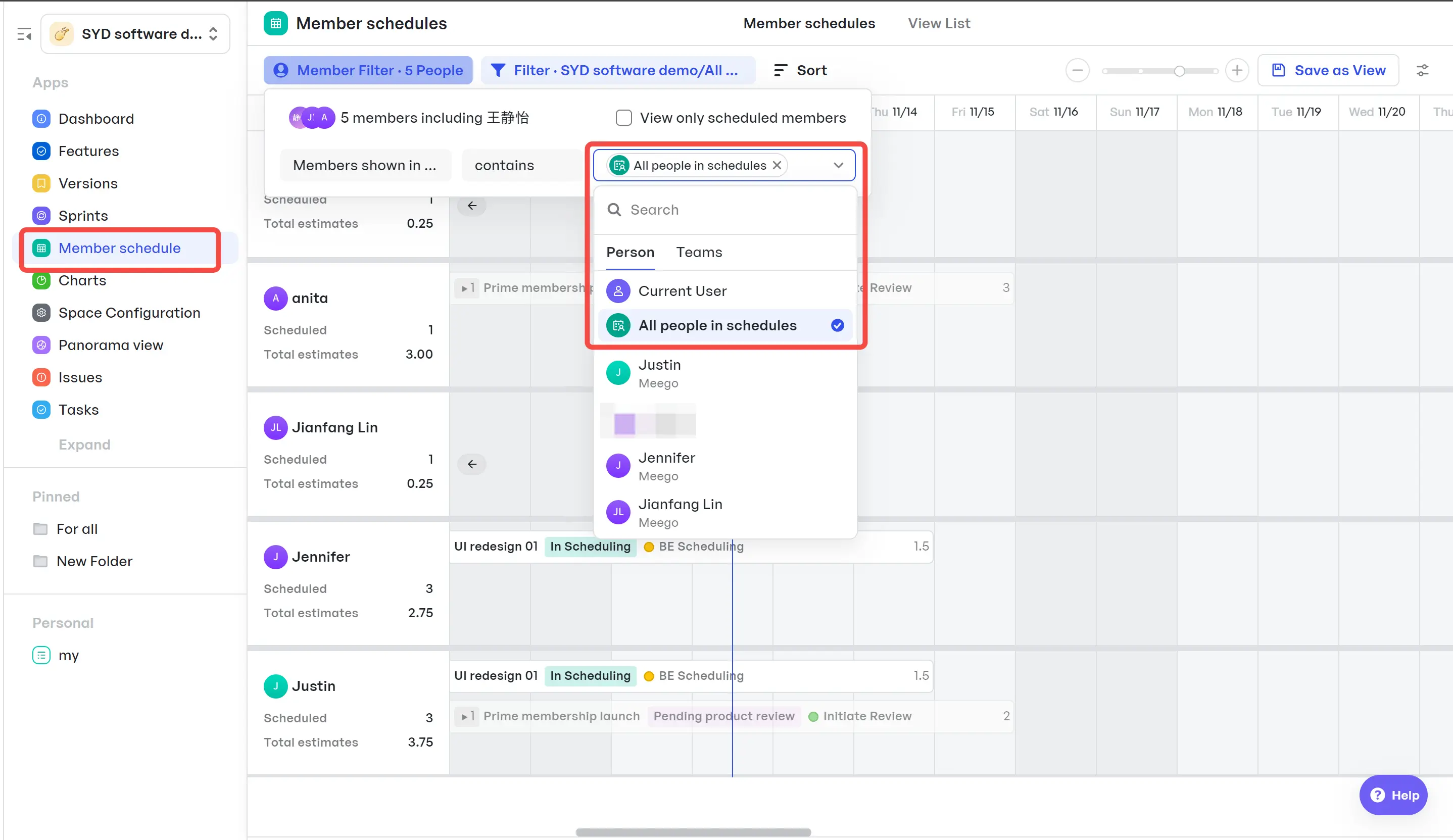 Checking project team members' schedule
Checking project team members' schedule- Teams can define milestones as subtasks or linked events in the Gantt chart. They can also set dependencies between tasks, ensuring milestones reflect progress.
- Teams can create risk lists as dedicated attachments or sub-nodes within the Planning phase. They can also upload risk registers, assign owners for mitigation, and track updates through the node's lifecycle.
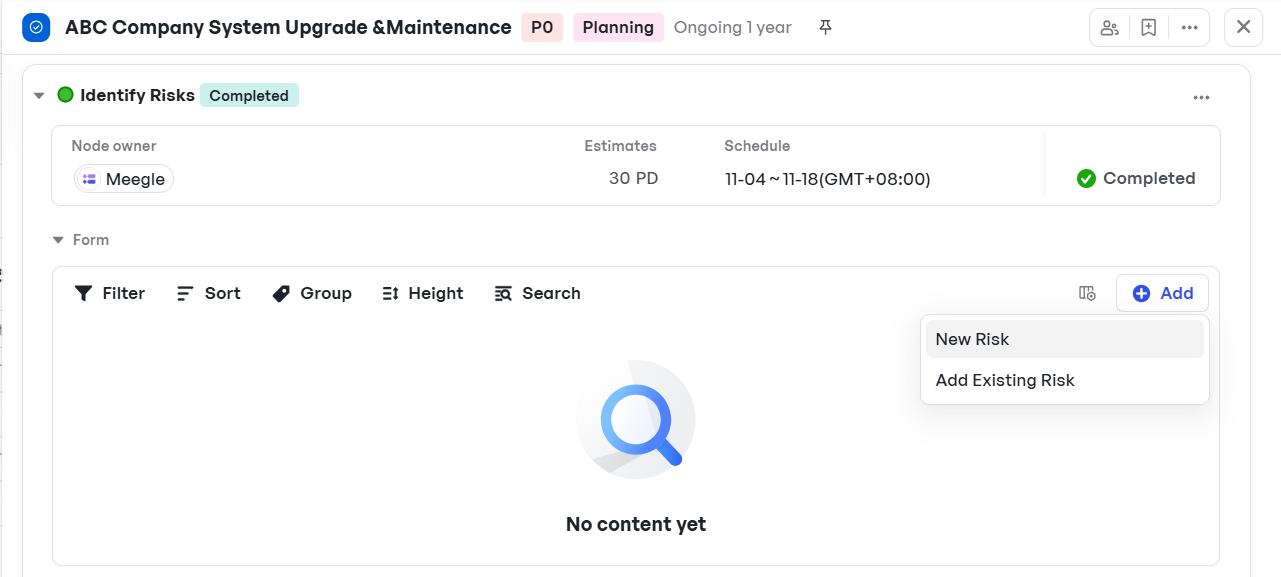 Adding new risks to dedicated risk lists
Adding new risks to dedicated risk listsInstead of juggling spreadsheets, sticky notes, and email threads, Meegle becomes your one-fit-all tool for smooth collaboration.
For further reading:👉What is Project Planning & How to Create One in 2025?
Phase 3: Execution
Execution is where plans become project deliverables. Once the planning phase wraps up, the real work begins: teams start executing tasks, collaborating cross-functionally, and bringing the project to life.
What's the goal of this phase?
To drive project progress, deliver outputs, and hit milestones—on time and within scope.
What happens during Execution?
As the most active and resource-intensive phase of the project lifecycle, tasks here typically include:
- Assigning and completing project tasks
- Cross-department collaboration
- Ongoing problem-solving and troubleshooting
- Updating timelines based on real-time progress
- Communicating with stakeholders and reporting on the status
The entire project team is involved here—designers, developers, marketers, QA, operations, and more (depending on the project). The project manager oversees coordination, resolving roadblocks, and ensuring continuous momentum.
Related read:��What is Project Collaboration: 6 Tips You Need to Know
How does Meegle help?
In Meegle:
- Node-driven workflows automate transitions between departments or roles. For example, once the design node is marked complete, Meegle auto-notifies the development team and opens the next task, eliminating the need for manual follow-ups.
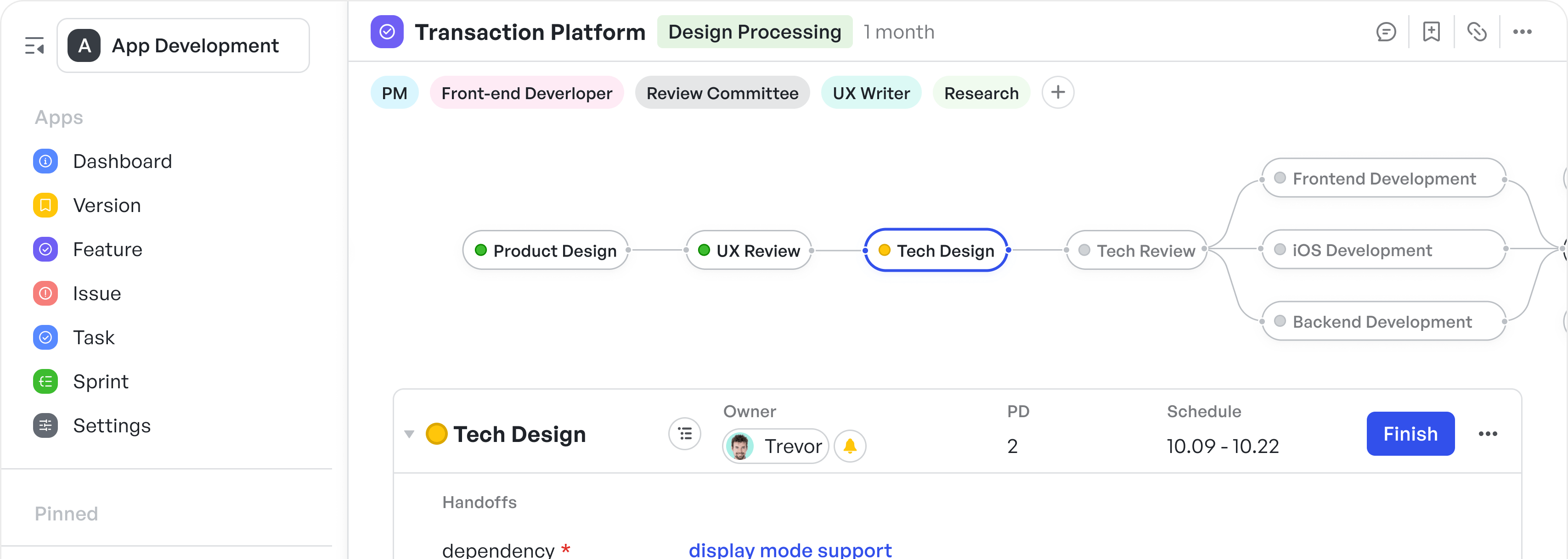 Sample node workflow for software development
Sample node workflow for software development- The Dedicated Issues work item supports issue tracking within each work item. Teams can flag problems, assign resolution owners, and log resolutions without switching tools.
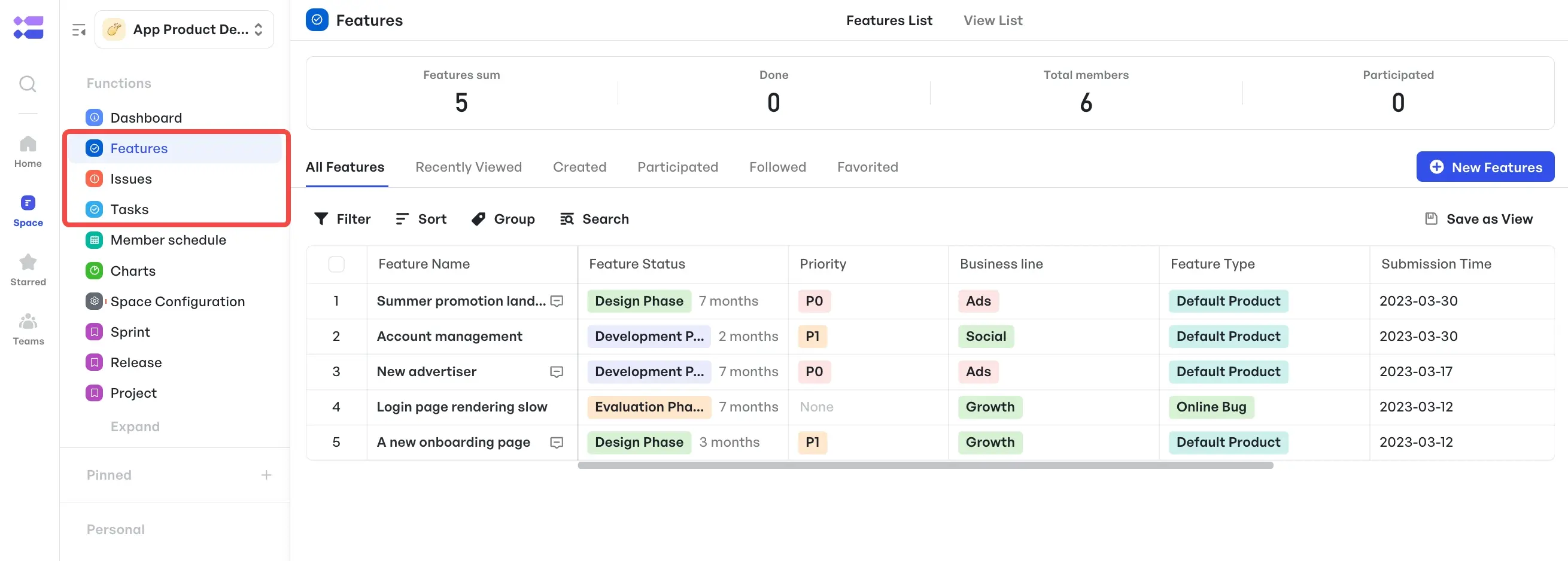 Issues work item for on-going problem solving
Issues work item for on-going problem solving- Each work item in Meegle's Execution workflow node contains a structured set of subtasks, dependencies, and attachments. Teams can mark progress at the task level, update statuses (e.g., In Progress, Blocked, Done), and collaborate within the task feed to maintain workflow momentum.
- Deliverables can be attached directly to work items or nodes. Meegle also records version history, discussions, and completion timestamps for traceability.
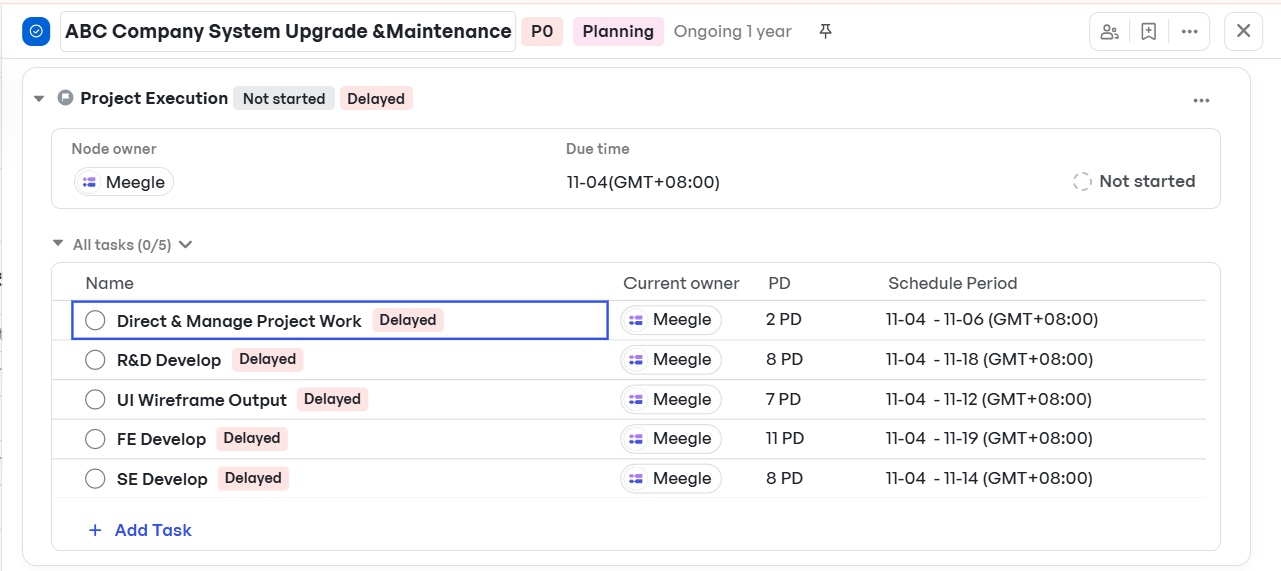 Schedule and timestamps for deliverables
Schedule and timestamps for deliverablesIn Execution, speed and coordination are everything. Meegle enables both by cutting the busywork, eliminating handoff friction, and keeping everyone aligned from kickoff to final output.
Phase 4: Monitoring and Controlling
Project Monitoring runs alongside the Project Execution Phase. While teams focus on deliverables, PMs monitor progress, risks, and alignment, making adjustments as needed to keep the project moving forward.
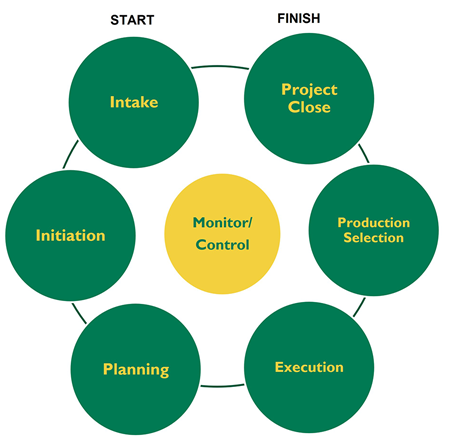 Monitoring and Controlling phase (Source: NSU OIT)
Monitoring and Controlling phase (Source: NSU OIT)What's the goal of this phase?
Monitoring is all about early detection—spotting issues before they become blockers. So, the goal is to ensure the project stays on schedule, within budget and scope, and aligned with company goals.
What happens during monitoring?
This phase is all about oversight, adjustments, and communication. Key tasks include:
- Tracking task completion and project performance
- Updating Gantt charts or timelines as work progresses
- Reviewing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and deliverable quality
- Reassigning resources or shifting priorities when needed
- Sending updates to stakeholders or clients to maintain transparency
The primary players in this phase are project managers and team leads, who need real-time visibility and fast feedback loops to make smart, timely decisions.
How does Meegle help?
In Meegle:
- PMs can use task filters and progress views to run effective check-ins. They can filter by owner, due date, or task status to quickly spot delays or blockers.
- Real-time dashboards provide an up-to-date view of task progress, completion rates, and timeline adherence. Teams can also use Gantt Views to compare actual timelines with planned schedules at a glance.
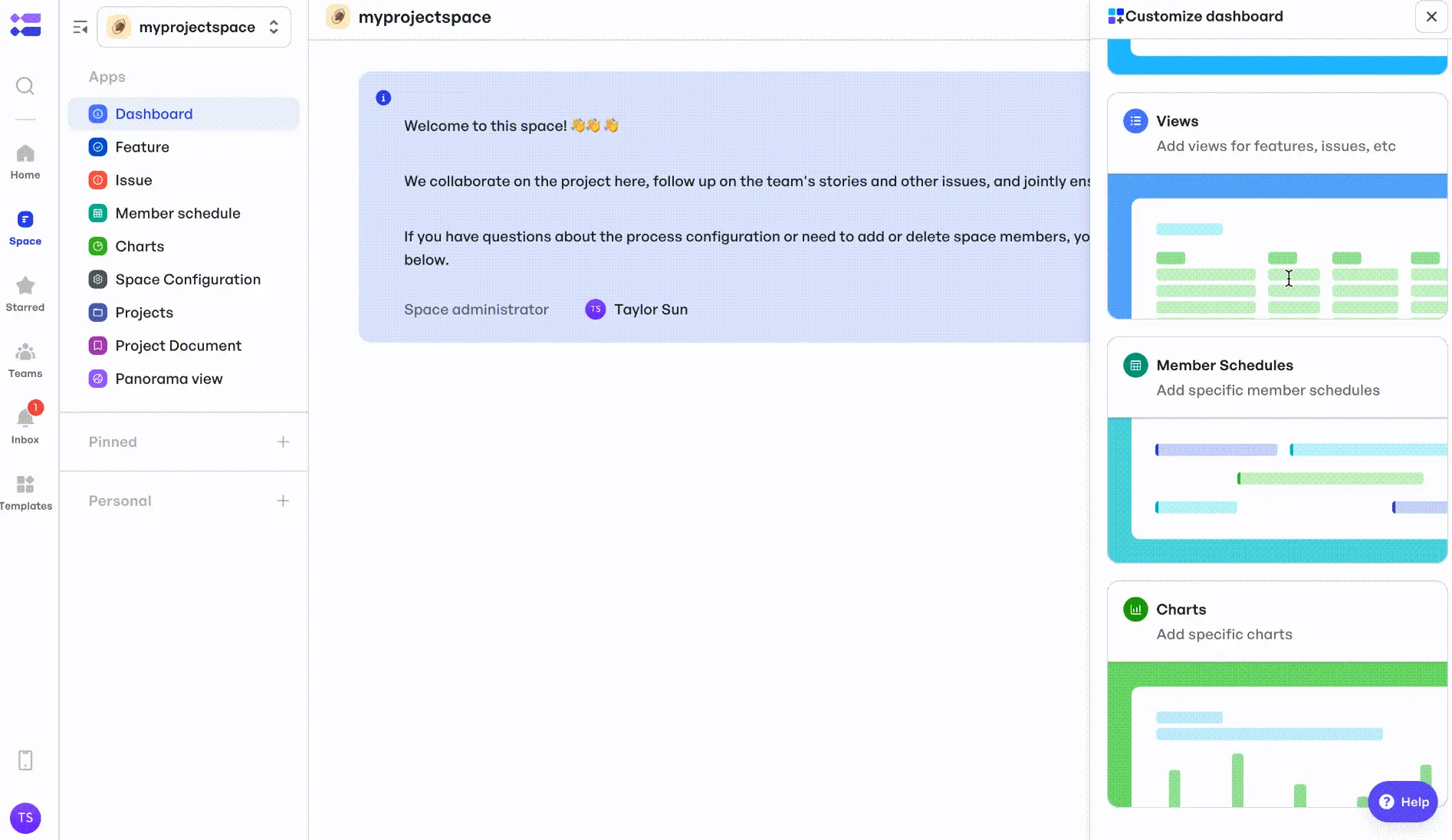 Meegle's customizable dashboard
Meegle's customizable dashboard- PMs can highlight stalled nodes or delayed work using delay labels. They can drill into delayed items, reassign tasks, or trigger internal escalations—all from one view.
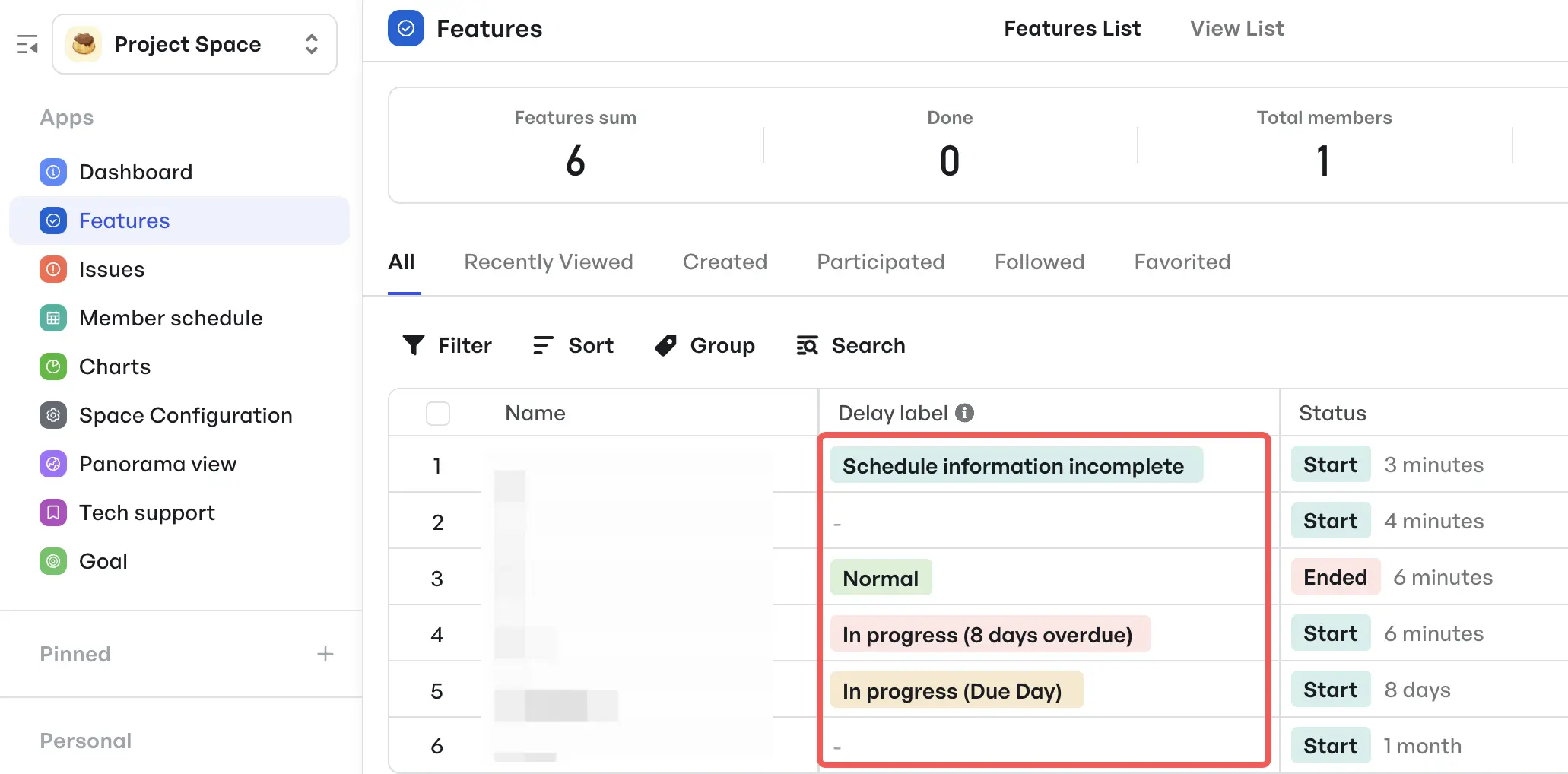 Real-time updates on project with Meegle
Real-time updates on project with Meegle- Custom alerts can notify stakeholders when tasks exceed time limits, workloads spike, or key milestones are at risk. Alerts go directly to the Inbox, making issue detection fast and centralized.
- Changes can be logged as new nodes or tasks and routed through Meegle’s workflows for review and approval. PMs can also compare baseline plans against updated scopes using dashboard charts for transparent decision-making.
- Bar charts, pie charts, and cumulative progress views help visualize project health by task status, phase, or owner. Reports can be shared with leadership or stakeholders during check-ins for quick, informed updates.
Instead of playing catch-up, Meegle helps teams stay ahead, shifting monitoring from reactive damage control to proactive project excellence.
Phase 5: Closure
The project closing phase marks the formal end of the project management lifecycle, where teams capture lessons for future growth.
What's the goal of this phase?
To confirm project completion, assess outcomes, and document insights for future projects.
What happens during Closure?
The Project Closure phase is part wrap-up, part reflection. Common tasks include:
- Securing final approvals from clients or stakeholders
- Handing off deliverables to operations, support, or end-users
- Running retrospective meetings to gather feedback
- Conducting performance evaluations
- Archiving documentation for future reference or audits
- Celebrating milestones and team achievements
Project managers typically lead this phase with support from the PMO, sponsors, and relevant department heads. It's a collaborative pause to reflect, learn, and reset.
Suggested read:��Stakeholder Management in Project Management: Strategies & Tools
How does Meegle help?
With Meegle's Charts and dashboards, teams can visualize performance metrics, highlight wins, and generate reports for stakeholders—all in one centralized space.
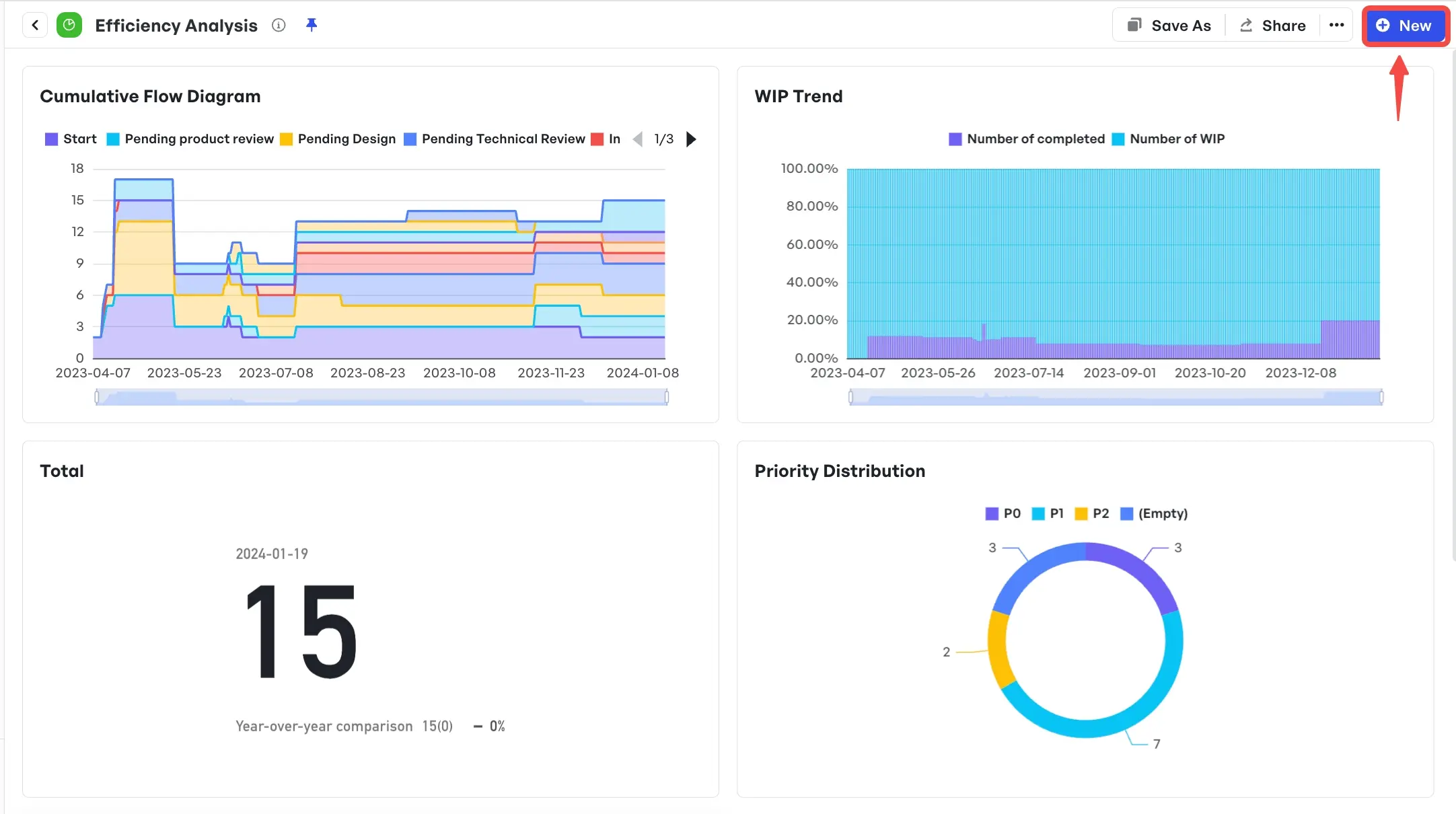 Efficiency report for closure
Efficiency report for closureIn Meegle, you can:
- Review project KPIs across phases using the Efficiency Analysis report
- Share wrap-up reports with clients or executives
- Archive workflows and decisions for future reference or audits
- Replicate successful structures for upcoming projects
Planning your project phases with Meegle
Meegle helps teams break complex projects into structured phases using its Project Life Cycle template. Whether you're managing a product launch, internal initiative, or client delivery, Meegle keeps everything organized, visible, and moving.
The project life cycle template
This template comes fully equipped with everything (node-driven workflows, preset work items, and automation tools) teams need to manage a project from Intake to Closure.
Workflows
Each phase of the project is visually mapped into nodes and tabs, offering a structured approach to task management from day one.
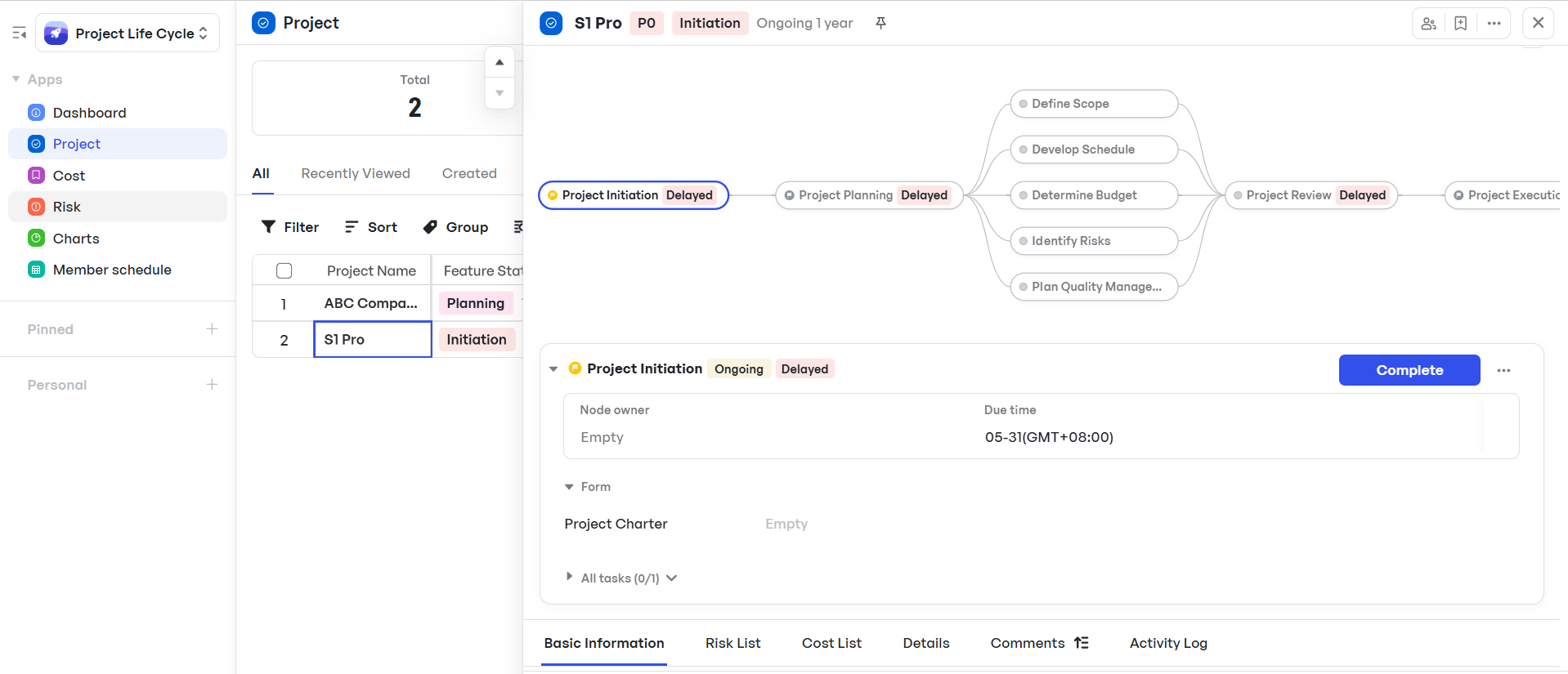 Structured task management with Meegle
Structured task management with MeegleUnder Basic Information, the space owner (typically the project manager) can set milestones and assign owners using the Roles and Members button.
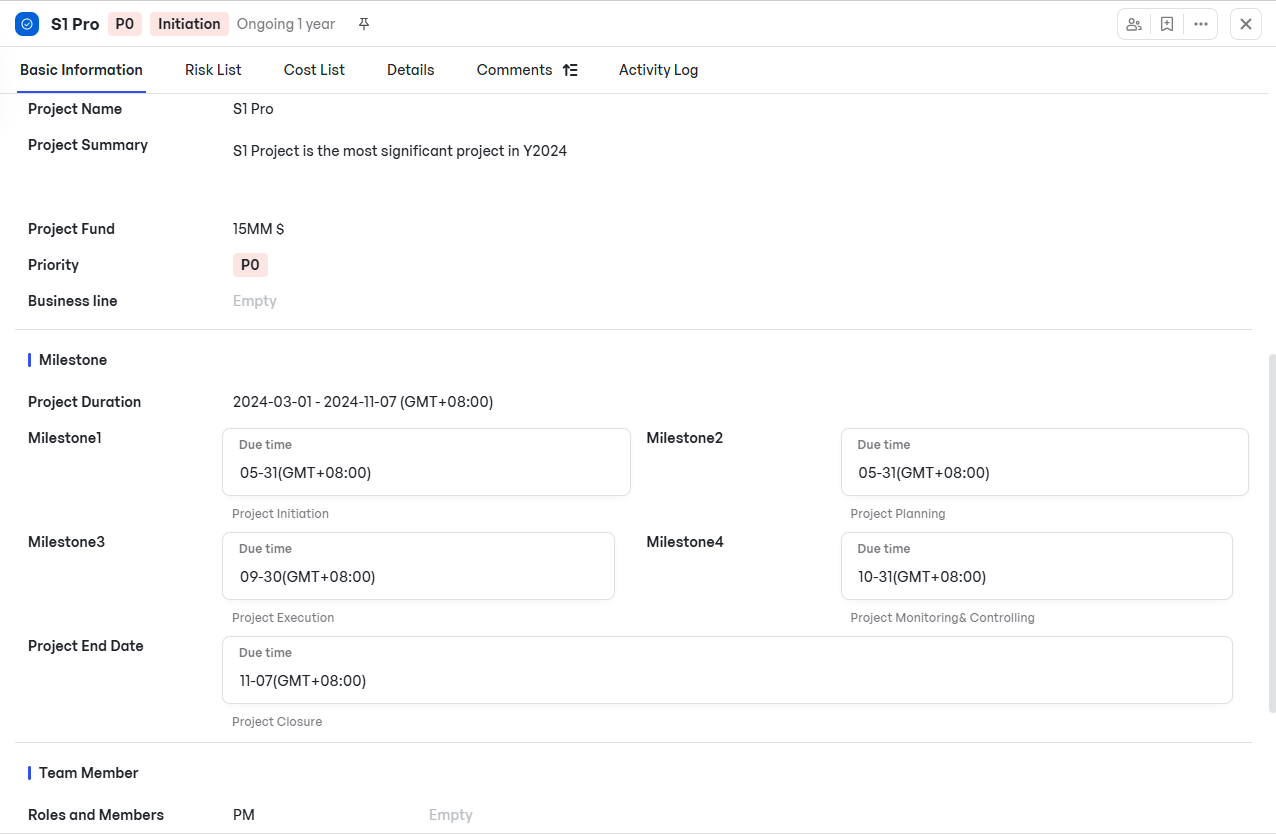 Setting milestones and assigning responsibilities
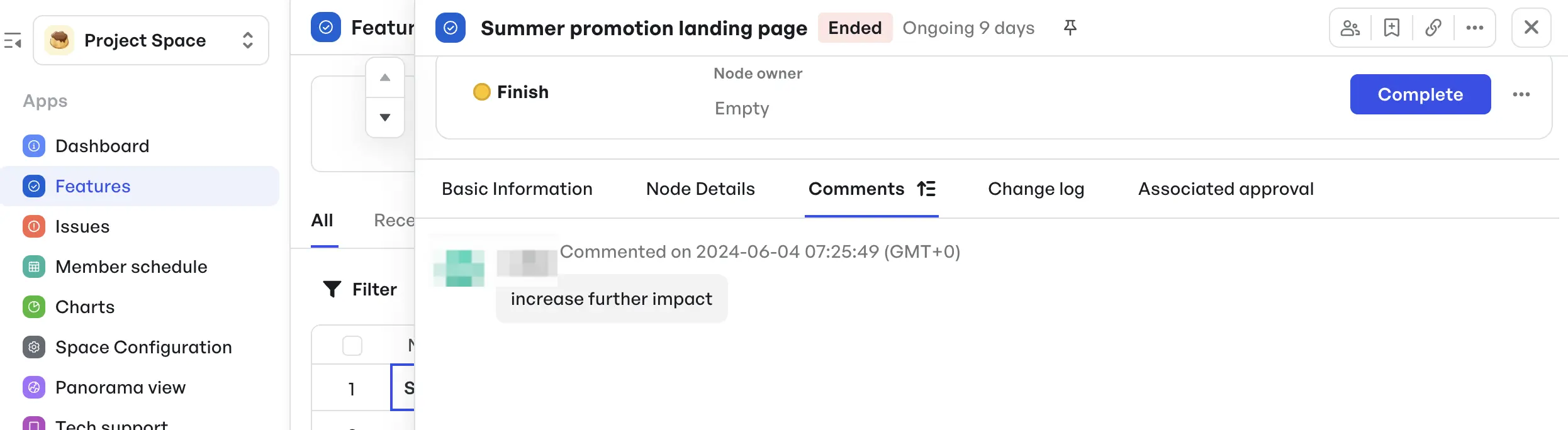
Setting milestones and assigning responsibilitiesTeam members can also use the Comments tab to collaborate in real time across all phases—no need to switch tools or chase updates.
The template includes preset work items that keep project components linked and organized:
- Project: Manages the project life cycle phases in node-based workflows
- Risk: Tracks risk exposure connected to the core project node
- Cost: Manages budget and financials, also tied to the project
- Tasks: Subtask management within individual nodes
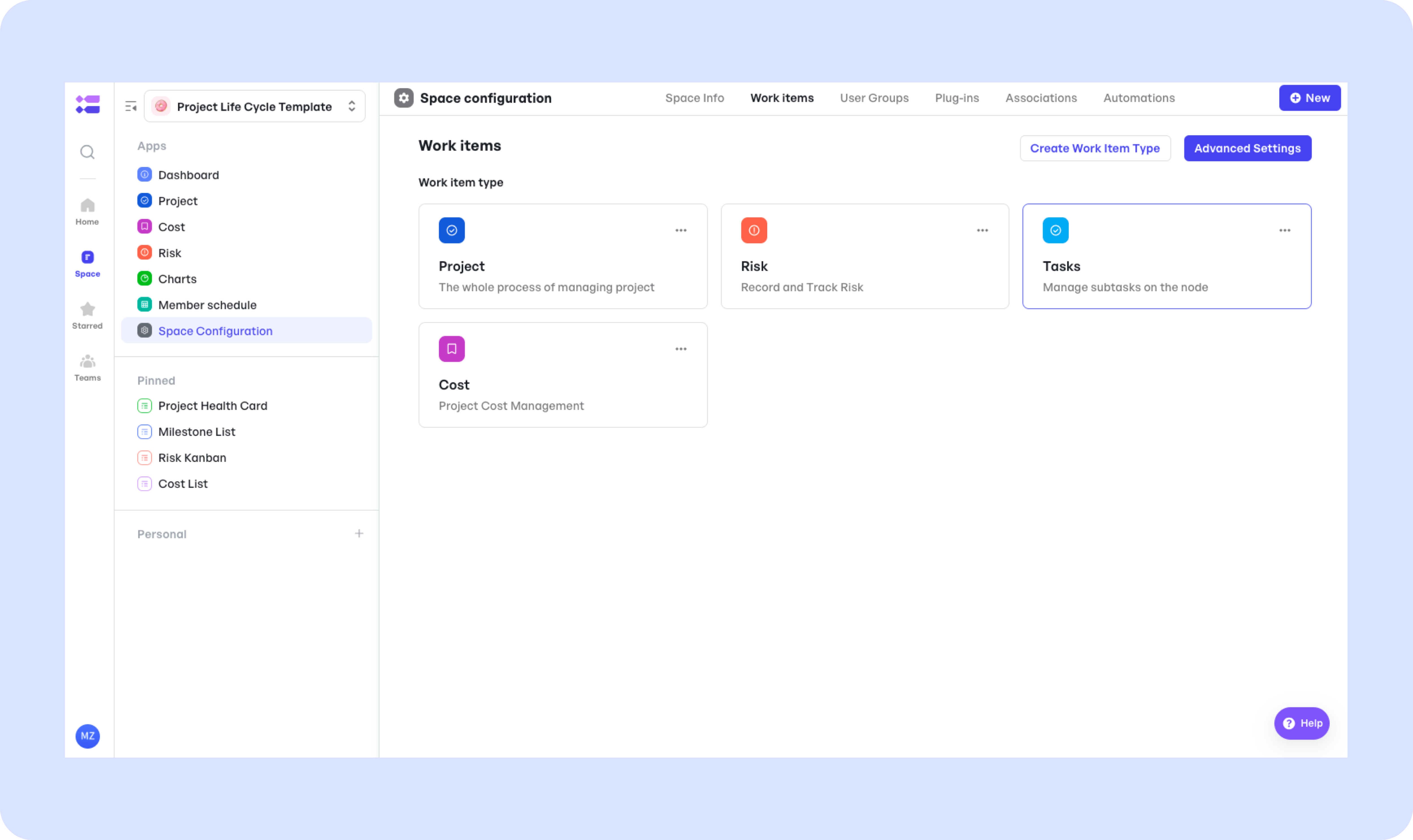 Preset work items for teams
Preset work items for teamsYou will also get access to tools like Dashboards, Charts, and the Member Schedule to visualize dependencies, manage bandwidth, and avoid scope creep in one centralized workspace.
Meegle helps teams automate repetitive actions and task handoffs, saving time and ensuring nothing slips through the cracks.
For example, you can:
- Automatically notify the team of changes to scope, timeline, or assignments
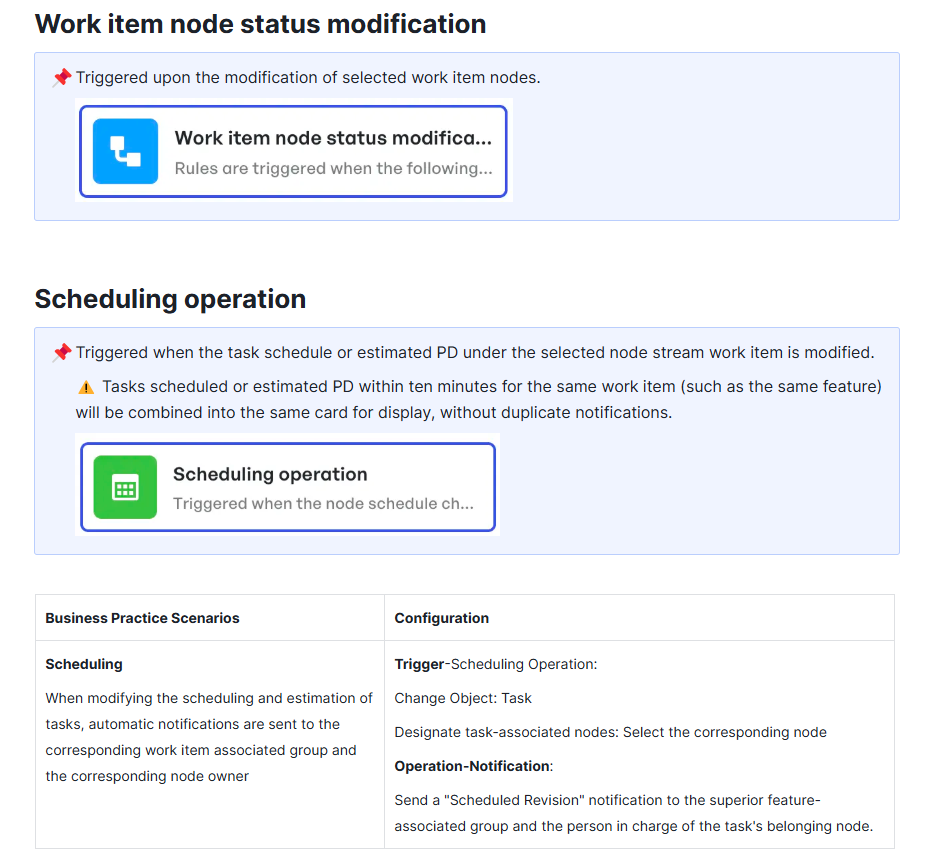 Automating node status modifications
Automating node status modifications- Instantly alert team members when there are revisions to their tasks
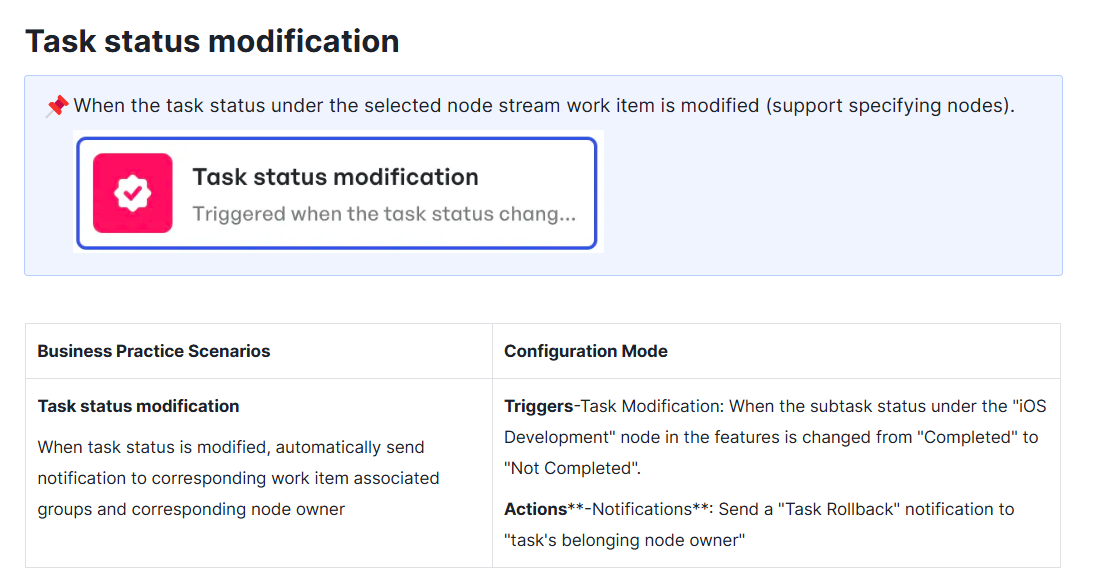 Automating task status modifications
Automating task status modificationsUsing Meegle leads to faster response times, fewer delays, and better alignment across the project lifecycle, as revealed by real teams:
- Lizhi accelerated product releases by 50%
- Skylink now consistently delivers games on time and budget
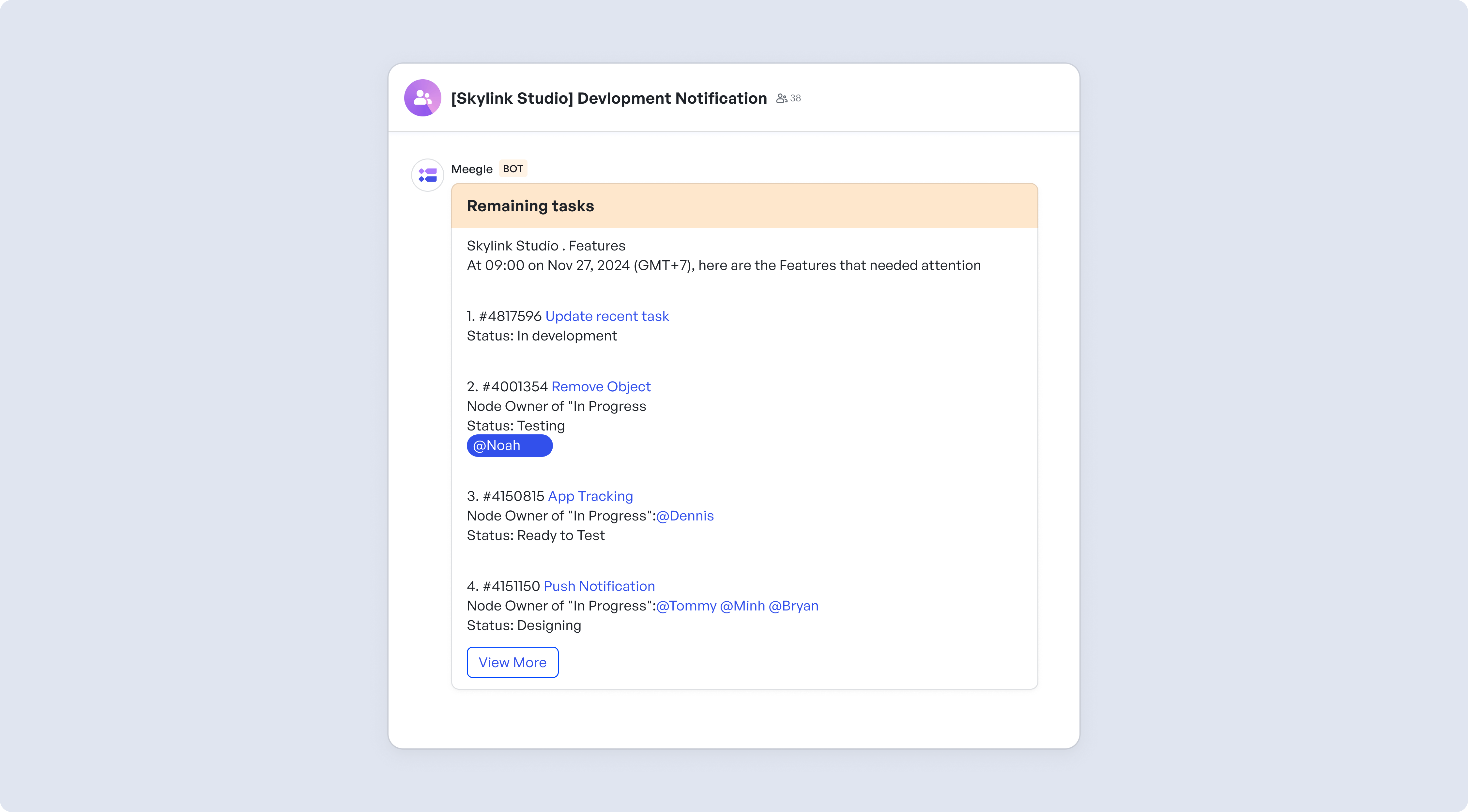 Meegle automation in action
Meegle automation in actionYou can achieve similar results when you manage your projects with Meegle.
Master every project phase with Meegle. Sign up for free and get moving.
FAQs
How do project phases differ from project milestones?
Project phases represent stages of work (e.g., Planning, Execution), while milestones are specific events or achievements within those phases (like "Prototype approved" or "Budget finalized").
Can project phases overlap in real-world projects?
Yes. In many agile or hybrid models, phases like Execution and Monitoring often run in parallel to allow for faster iteration and continuous improvement.
Which phase is most critical for project success?
While all phases matter, poor planning often leads to misalignment, scope creep, and missed deadlines. A well-structured Planning phase sets the foundation for smoother Execution and Monitoring.
How do tools like Meegle support multiple project phases?
Platforms like Meegle use visual workflows, Gantt Charts, dashboards, and issue tracking to support and connect tasks across all phases—from Intake to Closure—ensuring seamless transitions and visibility.
The world’s #1 visualized project management tool
Powered by the next gen visual workflow engineRead More
Check All BlogsStart creating impactful work today