9 Product Manager Goals to Focus on in 2025

Product management has evolved significantly, thanks to the integration of AI, demand for sustainability, and a sharper focus on customer-centric design.
Quite similar to how our values and ambitions advance with new experiences, so too do the goals of product managers. Staying relevant, hitting KPIs, and leading high-performing teams today requires rethinking how goals are set and what they’re aiming for.
Ten years ago, you’d hear more about Management by Objectives (MBOs) – a top-down, static framework that was often disconnected from how a product actually works. But today, the shift is toward Objectives and Key Results (OKRs). A more agile, transparent, and structured approach that reflects how product work (and users) have evolved.
This article breaks down modern product management goals and introduces Meegle, a product management software designed to help PMs:
- Set product goals that match changing user and business needs.
- Apply proven goal frameworks with real-world examples.
- Align teams, track progress, and deliver measurable outcomes.
To answer the above question, we first need to understand why the goal-setting process is changing, and why it is important in 2025.
What are Product Manager Goals?
Product Manager Goals are clear, measurable outcomes that guide a product manager’s efforts toward delivering business value, improving customer experience, and achieving strategic product success.
They typically align with broader business objectives and focus on areas such as:
- Product performance (e.g., increase user retention by 15%)
- Customer outcomes (e.g., reduce onboarding time by 20%)
- Team collaboration (e.g., improve cross-functional alignment in sprints)
- Market impact (e.g., launch three high-impact features by Q4)
In essence, PM goals act as a compass—helping prioritize tasks, make trade-offs, and evaluate progress throughout the product lifecycle.
Suggested Read:👉The Main Stages of the Product Management Process
Why is it important to set Product Manager Goals?
Product manager goals are important because they provide direction, focus, and accountability in a role that merges strategy, execution, and customer needs.
Here is how they benefit product managers:
- Strategic alignment – Ensures product decisions support broader business goals
- Focused prioritization – Helps PMs choose high-impact tasks over distractions
- Measurable progress – Tracks outcomes to evaluate success and guide improvements
- Cross-functional clarity – Aligns teams with a shared understanding of purpose
- Skill development – Supports the PM’s own growth through goal-driven learning
- Stakeholder confidence – Builds trust by showing clear direction and accountability
Changing trends in product management in 2025
Goals for product managers in 2025 need to change because of new trends in technology, security, and how teams work.
- Most companies now use AI, with 92% of product teams at some point testing AI tools and almost half having at least one use case. That means PMs must set goals to find real value from AI, not just try AI for the sake of it.
- As more businesses move to “as-a-service” models, product managers should aim to build shared platforms and reusable components, working with engineers so products scale faster and cost less.
- New AI features mean new ways for things to go wrong – and new challenges for security teams. PMs need security-focused goals from the start and close collaboration with security teams.
- Finally, with teams spread across locations and new roles like product operations growing, goals should focus on clear communication, shared responsibility, and keeping everyone on the same page.
Read more about the emerging trends in product management in 2025 to better understand the shift—and how traditional and modern product manager goals compare.
| Aspect | Traditional PM goals | Modern PM goals |
|---|---|---|
| Success metric | Deliver features on time | Deliver measurable business outcomes (e.g., retention, revenue) |
| Process Approach | Waterfall, linear project management | Agile, iterative product development |
| Primary focus | Internal stakeholder requirements | Deep customer understanding and problem discovery |
| Delivery mindset | One-time launches | Continuous delivery and iteration |
| Collaboration style | Siloed handoffs between teams | Cross-functional team leadership and alignment |
| Role expectation | Tactical execution (specs, backlogs) | Strategic ownership (vision, market fit, scaling) |
| Tooling | Gantt charts, PRDs, status reports | User research tools, analytics, A/B testing platforms |
| Metrics tracked | Features shipped, project completion | Business KPIs: NPS, churn, TTV, engagement, ARR |
| Timeframe | Short-term project cycles | Long-term product lifecycle ownership |
| Influence | Team-level contributor | Organization-wide impact and decision-making support |
This progress shows a broader evolution in the product role, from a task-driven contributor to a strategic leader who shapes the product’s direction and achieves measurable results. To set goals that really create impact, product managers need a structured framework; one that brings clarity, focus, and accountability to the work.
The SMART goal framework for product managers
Modern product managers use the SMART framework to turn broad ambitions into focused, actionable goals.
 The SMART goal framework for product managers
The SMART goal framework for product managersWhat are SMART goals for product managers?
The SMART goal framework helps product managers set goals that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound, ensuring clarity, focus, and accountability in product outcomes.
Each letter stands for a key trait that makes a goal more likely to succeed:
1. Specific
Goals should be clear and well-defined, not vague or general.
For example: Instead of saying “Improve onboarding,” a specific goal would be: “Redesign the onboarding flow to reduce drop-off before account creation.”
You can improve onboarding in your organization with Meegle's onboarding template
2. Measurable
You need to know if you’re making progress. Measurable goals include concrete metrics.
For instance: “Increase the onboarding completion rate from 65% to 85% in Q2.”
3. Achievable
Ambitious is good, but unrealistic goals set teams up for failure. Goals should stretch the team without overwhelming it.
For example: If your current NPS is 30, aiming for 50 in one quarter might be achievable. Aiming for 90 likely isn’t.
4. Relevant
Every goal should tie back to broader product or business objectives.
- For instance: “Improve activation rate” is relevant if your company’s priority is user retention. “Add dark mode” may not be, except it's tied to customer complaints or churn.
5. Time-bound
Deadlines create urgency and help with planning. A goal without a timeline is just a wish.
For example: “Launch the new dashboard experience to 100% of users by the end of Q3.”
SMART vs. Non-SMART goals examples
| Non-SMART goals | SMART goals |
|---|---|
| Make the product better | Improve user satisfaction score from 4.1 to 4.5 by September |
| Increase revenue | Grow monthly recurring revenue by 15% in Q2 through upsell campaigns |
| Get more users | Increase daily active users from 10K to 15K by July 30 |
When done right, SMART goals give your team direction, focus, and a shared definition of success.
Now that we’ve covered how to structure goals, let’s look at the product manager goals you should focus on in 2025, along with examples and metrics that make them actionable.
9 Product manager goals to set in 2025 (with examples)
Based on the above trends, here are some important and SMART product manager goals for 2025, along with strategies to improve overall product development, team collaboration and finding the perfect product market fit. The focus has shifted toward goals that balance business growth, user needs, and internal alignment.
How do you actually achieve these outcomes?
Here are nine product managers goals you should set this year:
- Improve product-market fit
- Increase overall customer satisfaction and engagement
- Drive product strategy with data-driven insights
- Enhance cross-functional collaboration
- Optimize product adoption and retention
- Align product roadmap with strategic business goals
- Develop advanced data literacy
- Enhance leadership and influence
- Build product innovation capabilities
To understand the "why" behind setting these goals, here's a full breakdown.
Goal 1: Improve product-market fit
Why set this goal? Without product-market fit, you’re building for everyone and satisfying no one.
One of the most important product manager goals in 2025 is ensuring your product clearly solves a defined user need.
In fact, according to a report from CB Insights, 42 percent of startups fail because they never nail a real market need. That's why you should never guess what users want.
You need a continuous feedback loop between user insights, prioritization, and product decisions. PMs who build this loop are better positioned to reduce churn, strengthen engagement, and ship features the market actually needs.
Key metrics to track:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Activation rate
- 30-day churn rate
- Frequency of “setup confusion” mentions in support tickets
SMART goal example: Interview 50 users from 3 core target segments by end of Q3 to validate top problems, and run 2 prototype tests to confirm problem-solution fit before finalizing Q4 roadmap.
Once you’ve validated product-market fit, the next challenge is deepening your relationship with users.
Suggested Read:👉11 Product Management KPIs in 2025 [+ How to Track Them]
Goal 2. Increase overall customer satisfaction and engagement
Why set this goal? Happy, engaged users not only stick around – they become your strongest advocates.
Customer satisfaction and engagement impact both retention and WoM (word-of-mouth). Product teams must move beyond feature delivery to creating experiences that delight users at every touchpoint.
Customer satisfaction can be measured through:
- CSAT surveys - brief in-app polls after key actions
- User interviews - targeted, one-on-one feedback sessions
- Product usage data - average session duration and return frequency
SMART goal example: Improve CSAT for building and deploy workflows from 72% to 85% by Q4 by adding inline tips, pre-filled templates, and simplifying error messages based on top support queries.
Understanding engagement is one thing, using that data to improve decisions is the next.
Goal 3: Drive product strategy with data-driven insights
Why set this goal? Product decisions are only as strong as the data behind them.
As a product manager, you need to reduce intuition bias and make decisions based on how users actually behave – not how you hope users behave. Do this by setting up regular data reviews, comparing assumptions against actual usage patterns, and validating ideas through quick experiments before committing development resources.
Next, define performance goals for what to measure, when to review it, and how to turn insights into action.
Some performance goals can include:
- Running A/B tests on high-traffic workflows to validate UX changes
- Tracking feature adoption within 30 days of launch
- Correlating user behavior with churn risk signals.
It's basically about tracking the right things.
SMART goal example: Increase deployment flow completion from 62% to 80% by Q4 by tracking drop-offs and addressing the top 3 constraints surfaced in usage analytics.
Of course, no product strategy succeeds in isolation. To deliver on data-driven priorities, you must align the teams doing the work.
Goal 4: Enhance cross-functional collaboration
Why set this goal? Great products are built by aligned teams – not isolated functions.
A product's overall success depends on how well multiple internal teams work together. For product managers, this means setting collaboration goals that bring clarity across engineering, design, marketing, and customer success.
When communication breaks down, delays increase, and priorities change, it becomes difficult for teams to achieve their goals. To improve team alignment, product managers should define objectives tied to how teams work together.
Examples of collaboration objectives:
- Reduce feedback cycle time between product and engineering from 5 days to 2 days
- Co-create a launch plan for every major feature with the marketing team
- Improve spec clarity scores from 3.2 to 4.5 (measured via team pulse surveys)
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for this goal can include:
- Time to resolve cross-team dependencies
- Ratio of open to resolved roadmap items per team
- Team alignment scores (from regular surveys)
SMART goal example: Reduce rework from design-to-dev handoffs by 50% before the end of next quarter through structured kickoff sessions and clear task ownership in Meegle.
With teams aligned, your focus can shift to user behavior, specifically how well your product gets adopted and keeps users coming back.
Goal 5: Optimize product adoption and retention
Why set this goal? A product that’s not adopted can’t deliver value and won’t last.
Adoption and retention are two of the clearest signals that your product is solving real problems. It’s not merely about signups – but about helping users reach their first meaningful outcome, and then come back for more. You need them to activate, return, and build habits around your core value.
Start by setting goals around (UAR) new user activation rate: the point where users first experience value. If users sign up but don’t reach this milestone, onboarding needs attention.
To improve retention, start by understanding why users leave. Common causes include: unclear value, friction in repeated tasks, or lack of support. Proactively reviewing usage trends and running exit surveys can help you find root causes.
Metrics to track customer adoption and retention:
- New user activation rate
- Day-7 and day-30 retention rate
- Early-stage churn rate
- Onboarding drop-off percentage
- Feature adoption rates
SMART goal example: Increase new user activation rate from 45% to 65% by Q4 by updating onboarding to include a guided setup tour and pre-built pipeline templates.
While adoption focuses on individual users, your roadmap should also reflect where the business is headed.
Goal 6: Align product roadmap with strategic business goals
Why set this goal? When your product roadmap reflects company priorities, every sprint moves the business forward.
One of the most important product manager goals in 2025 is ensuring what gets built actually impacts business outcomes.
Too often, product teams fall into the “feature factory” trap – shipping constantly, but not strategically. To avoid this, product managers should tie roadmap decisions directly to company-level OKRs and business objectives.
Success metrics to track business alignment and impact:
- Percentage of roadmap items tied to business goals
- OKR completion rate
- Feature-level impact on churn, revenue, and activation
- Stakeholder alignment score
SMART goal example: Reduce churn by 15% in Q3 by prioritizing fixes to two abandoned workflows from churn feedback, and aligning 100% of roadmap items with company OKRs in Meegle.
These goals show how product management has evolved. Moving from output-focused tasks to outcome-driven impact.
But to lead effectively in this new environment, product managers should invest in their own growth.
Suggested Read:👉Product Roadmap Guide: What is it & How to Create One
Personal development goals for product managers
Personal development goals help you grow in ways that directly improve product outcomes and build long-term career value.
Here are three areas where modern PMs should focus their growth efforts.
Goal 7: Develop advanced data literacy
Data is the foundation of smart product decisions. Yet many PMs still rely too heavily on gut instinct. If you can learn how to ask the right questions and translate answers into action, you can guide teams toward the highest-value work.
How to set and achieve this goal:
- Audit and learn: Identify skill gaps (SQL, A/B testing) and enroll in one focused course.
- Apply what you learn: Create a live usage report in Meegle – track trends like activation or churn.
- Share insights: Present one takeaway in your team’s biweekly demo to practice learning.
Why set this personal goal? PMs who use data to guide decisions can prioritize goals more effectively, improve roadmap focus, and lead more confidently.
Goal 8: Enhance leadership and influence
Product managers lead through aligning teams, making decisions, and representing the user. You see why this is an important goal to set?
Here are some steps to help you improve leadership and gain influence:
- Build trust: Be consistent, transparent, and follow through on commitments.
- Communicate clearly: Test your presentations ahead of time to make them clearer and reduce questions.
- Create alignment rituals: Host a 15-minute “roadmap huddle” before each planning session – rotate who leads to encourage shared ownership.
- Collect feedback: After demos or planning, ask three colleagues for one thing you did well and one thing to improve.
Why set this personal goal? Leadership skills impact decision-making and build confidence across teams. When PMs lead effectively, they gain stakeholder buy-in.
Goal 9: Build product innovation capabilities
The purpose for innovation is to consistently find better ways to solve user problems and create room in your process for experimentation. One of the top goals for a product manager, right?
To build your innovation capacity:
- Make time to explore: Block dedicated hours each sprint for small experiments or early concept sketches.
- Study: Use Jobs-to-Be-Done interviews or simple Design Thinking exercises to understand user requirements.
- Talk to users: Run short, targeted interviews to learn where current workflows break down or feel slow.
- Validate early: Test ideas with a quick usability session or user poll before writing specs.
- Reflect and improve: Keep a “what worked/what didn’t” log. Review it quarterly to refine your process.
“Why set this personal goal? PMs who approach innovation with a repeatable process are better equipped to meet evolving user needs and respond to market shifts.”
Related read: 👉Project Managers Goals: 10 Examples
Setting goals based on your product lifecycle stage
The goals you set as a product manager should match your product lifecycle – whether you're in the early, growth, or mature stage. Each stage - early, growth, and maturity - comes with different challenges, success metrics, and priorities.
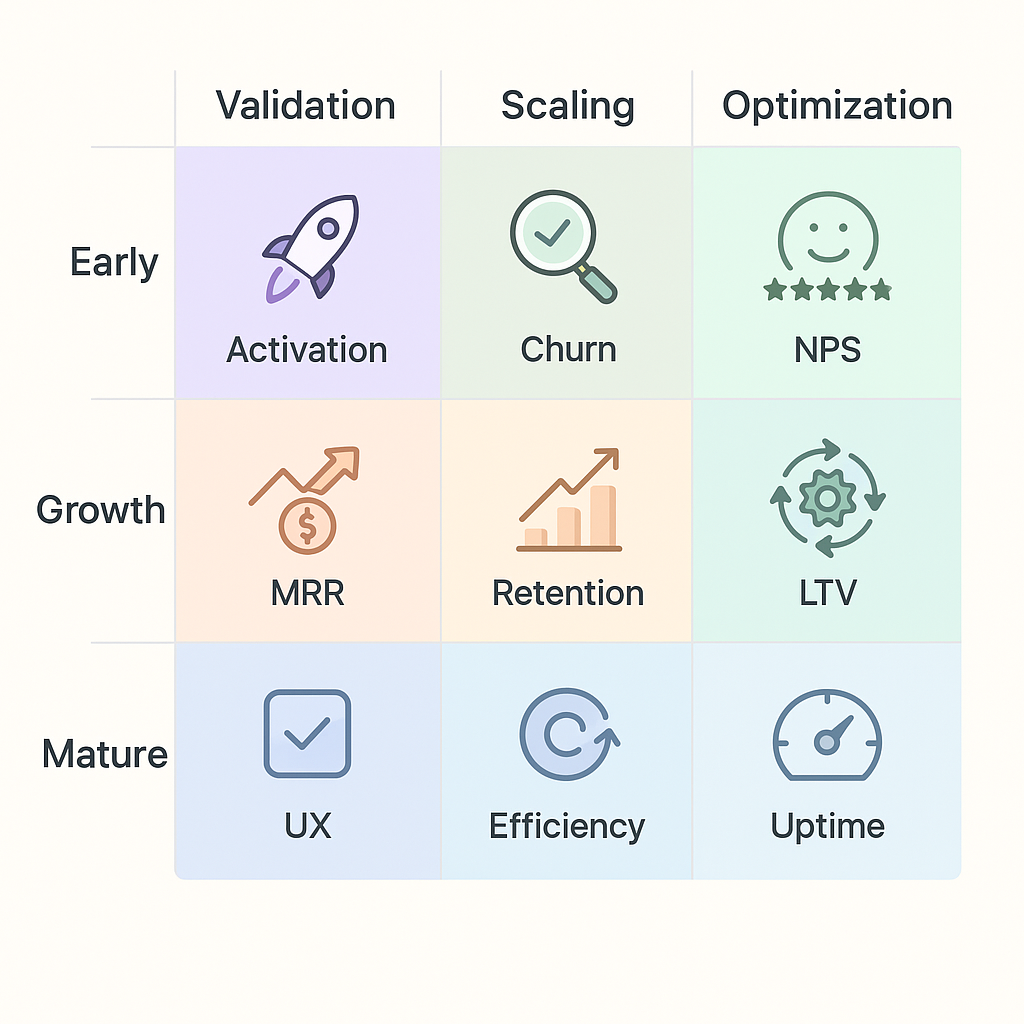 Setting product manager goals based on your product lifecycle stage
Setting product manager goals based on your product lifecycle stageWhat drives impact in the early stage may not work in the mature stage.
Product lifecycle goals overview
| Stage | Primary goal | Common challenges | SMART goal example | Key metrics | How Meegle helps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early stage (Pre-PMF) | Validate problem-solution fit and define core personas | Unclear user needs. Low activation. High churn | Reduce onboarding drop-off by 30% through guided setup improvements | Activation rate. Churn rate. Qualitative feedback volume | Document feedback, assign validation tasks, and track MVP testing visually with collaborative roadmaps |
| Growth stage | Expand reach and engagement | Prioritizing features. Scaling ops. Balancing speed vs. stability | Increase engagement on core feature set by 40% through UI updates | Weekly active users. Feature usage. NPS | Align cross-functional teams in Meegle using sprint boards tied to clear growth metrics |
| Mature stage | Optimize performance and expand revenue | Technical debt. Slowing growth. User churn | Increase upsell revenue by 20% through targeted feature enhancements | Retention rate. Revenue per user. Support ticket volume | Use dashboards to monitor performance, groom backlog, and improve team tracking |
By aligning your goals to your product’s stage, you focus your team’s energy on the outcomes that support progress and growth at that point in the lifecycle. As your product evolves, revisit and refine these goals to keep momentum strong and priorities clear.
Creating a goal-setting framework that works
Now that you have clear goals, how do you plan to execute them? Do you really have a system to manage them?
Here are three parts of a reliable goal-setting framework – complete with examples, practical tips, and ways Meegle can support your process.
Suggested read: 👉Best Goal Tracking Apps for 2025
Part 1: Implementing OKRs for product management
Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) are one of the most effective ways to align teams around outcomes, especially in companies scaling quickly. They help answer two questions:
- What do we want to achieve? (the Objective)
- How will we measure success? (the Key Results)
But writing good OKRs takes more than filling in a template. Let’s break it down.
1. Start with the outcome, not the task.
Instead of setting an objective like “Launch pricing page,” frame it around the result: “Increase trial-to-paid conversion by 15%.” That shift in focus gives your team clarity and flexibility in how to reach the goal.
2. Make key results specific and measurable.
Avoid vague targets like “Improve onboarding.” A better key result would be: “Increase onboarding completion from 65% to 85%.” You should be able to track progress without guessing.
3. Keep it focused.
Limit each team to 1–3 objectives per quarter. OKRs should never be a backlog – they’re a shortlist of what matters most right now.
To make this process easier, use Meegle’s OKR template to define, assign, and track your objectives in one place. It includes all the fields you need (owners, timelines, progress metrics), so your team stays aligned and accountable from day one.
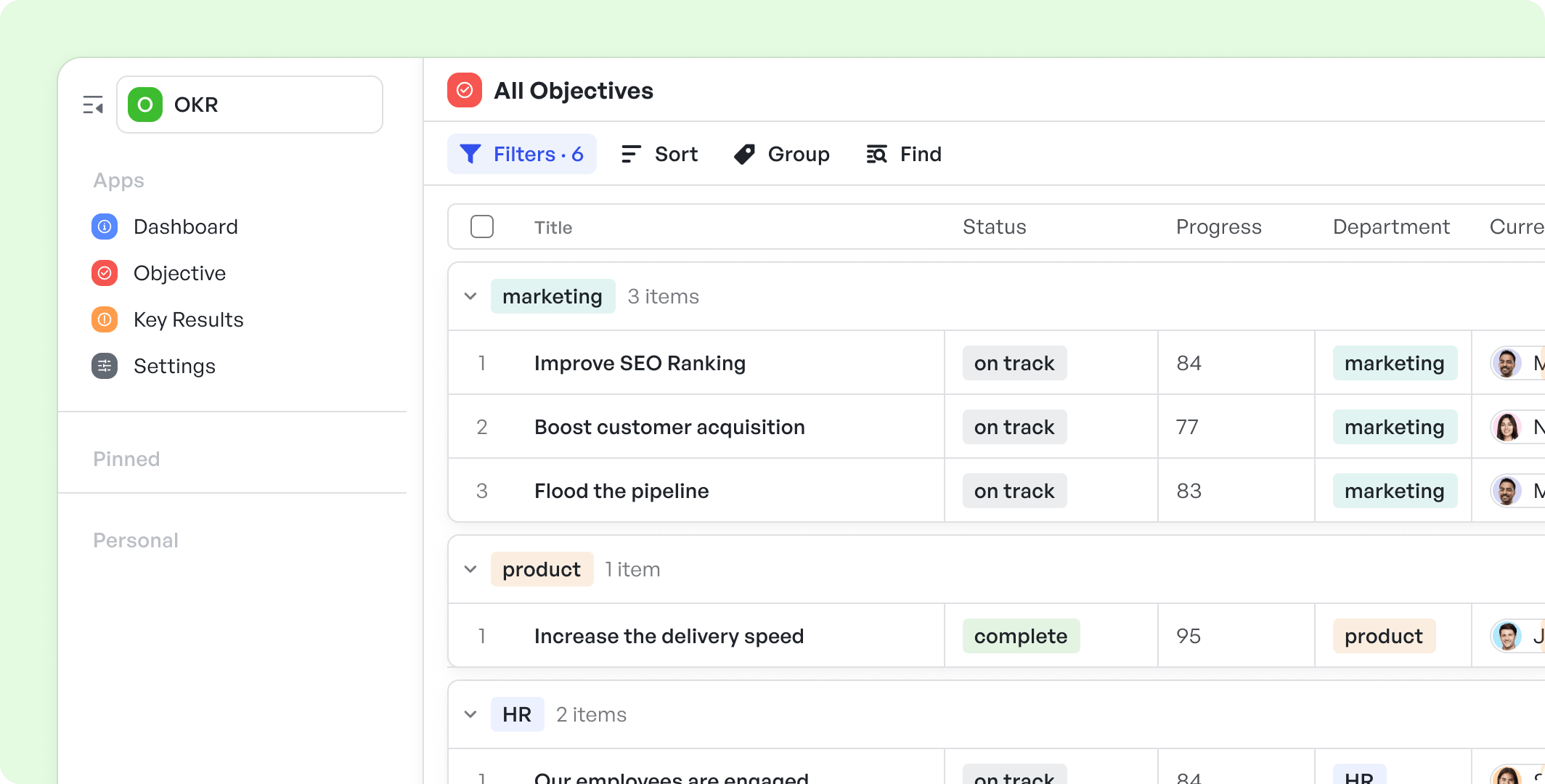 OKR template
OKR templateOnce your OKRs are in place, the next challenge is finding the right balance between ambition and feasibility.
Balance aspirational and achievable goals
A common mistake a PM can make is setting goals that are either too safe or completely out of reach. Neither helps. Effective OKRs should stretch your team without setting them up for failure.
The ‘hack’ is to aim for progress, not perfection. If you consistently hit 100%, your goals may be too easy.
An effective OKR should land somewhere around 70–80% completion. That leaves room to push boundaries while staying grounded in what’s possible. To keep momentum going, it’s just as important to check in regularly as it is to set the goal in the first place.
How to track and review OKRs effectively:
- Set a weekly or biweekly cadence for team check-ins
- Use Meegle’s OKR template to link key results to specific tasks, owners, and metrics
- Adjust timelines or scope if priorities shift – but document why
With OKRs working in the background, you can now focus on balancing short-term goals with long-term impact.
Part 2: Balancing short-term wins with long-term vision
It is true that not every goal needs to show immediate results. But without some sort of quick wins, stakeholders will lose faith in you. To help find balance between short and long-term goals, use timeframes to organize your goals:
- Quarterly goals: Help teams to focus and adapt quickly.
- Annual goals: Provide direction across longer cycles.
- Strategic > tactical: Every sprint goal should support a larger objective
For example, your long-term goal is to improve user retention. You can set a Q2 key result like “Increase day-7 retention by 10%,” then break that into sprint-level tasks like “Redesign onboarding flow to reduce drop-off.”
But this planning often involves trade-offs. When short-term fixes and long-term bets compete, use a simple impact vs. effort scale to prioritize. This keeps discussions objective and transparent. It also helps the team understand why certain goals move forward while others wait.
Frameworks should guide you, not trap you. That’s why you need a product management tool, specifically Meegle, that offers such flexibility. Meegle makes it easy to shift timelines, reassign tasks, and keep your plan updated without losing context.
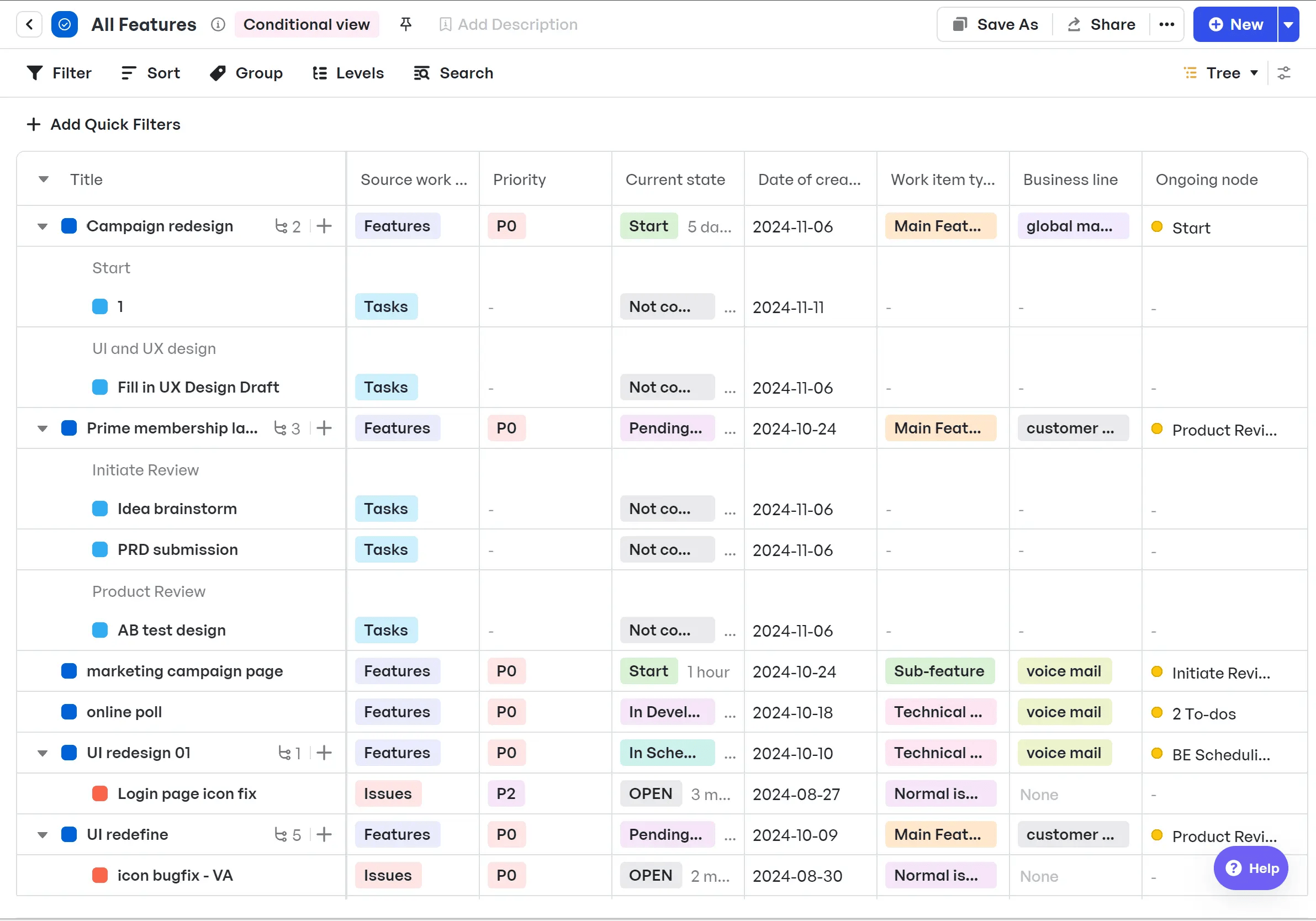 Keep plans updated with Tree View
Keep plans updated with Tree ViewPart 3: Involving key stakeholders in goal definition
You should never assume you outlined the best goal for the team in isolation. For goals to succeed, they need buy-in from the people who will help shape, deliver, or benefit from them.
Start by building shared understanding. Before writing goals, bring in key voices from product, design, engineering, and go-to-market teams. Regularly review user insights, performance data, or product strategy docs together.
Turn that shared context into collaboration:
- Host a lightweight goal-planning workshop
- Use a shared doc or board to co-write OKRs in real time
- Align on what “success” really means across roles
Stakeholder involvement doesn’t end at goal creation. You’ll need to keep them in the loop as the project progresses.
Make communication part of your process:
- Post active OKRs where everyone can see them
- Align goals during sprint reviews or retros
- Share brief progress notes in team channels or Meegle dashboards
 Space dashboard
Space dashboardWhen everyone understands the goals and how their work connects to them, they stay motivated, focused, and aligned.
How to prioritize and track your goals: step-by-step guide
Effective product manager goals depend on clear priorities and a reliable tracking process.
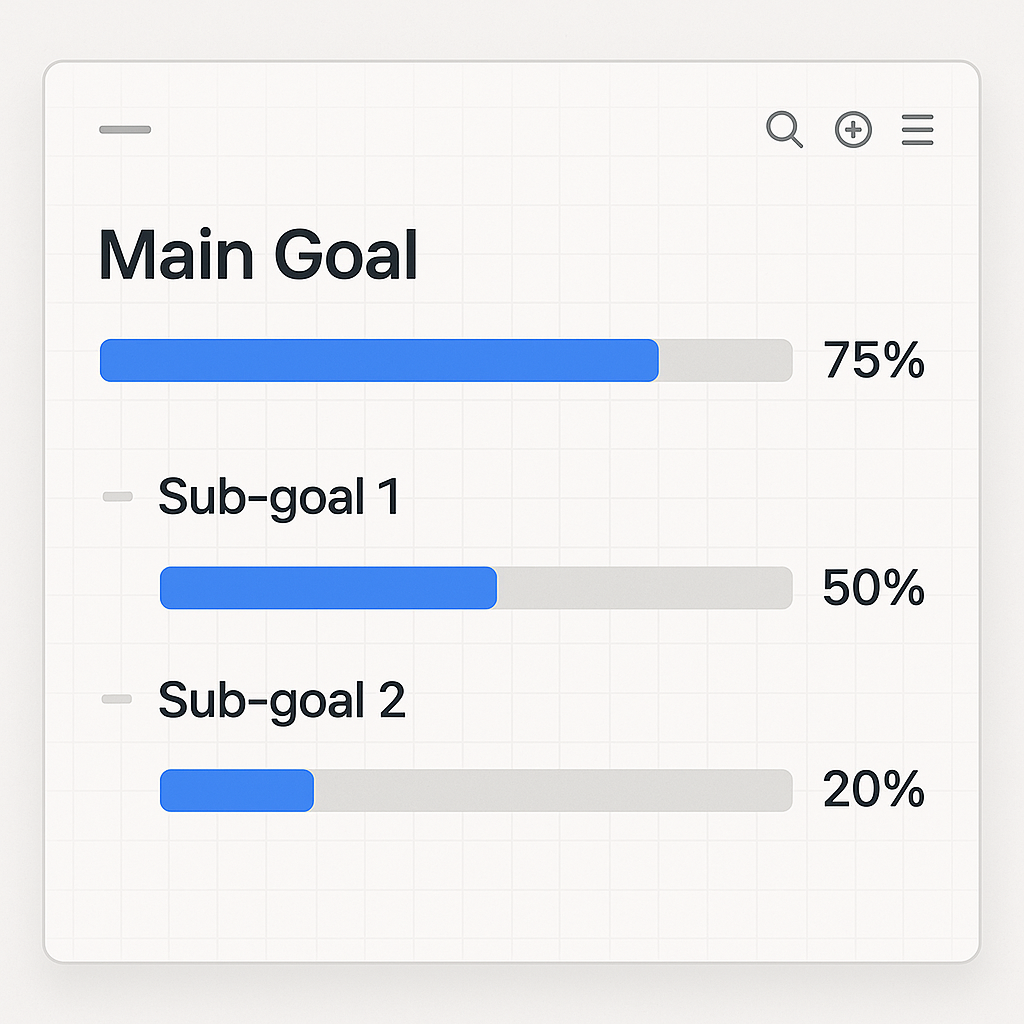
Step 1: Start with goal stacking
Begin by identifying one primary objective like boosting retention and then define two to three tactical sub-goals, such as improving onboarding completion or reducing time-to-value.
 Prioritize and track your goals
Prioritize and track your goalsGive each sub-goal a specific owner and tie it to a measurable success metric. For example:
- Day-7 retention → increase by 10%
- Onboarding completion → improve from 68% to 85%
- Support ticket volume → reduce by 15%
Step 2: Establish a check-in cadence
Next, decide how often you’ll check in. Weekly touchpoints work for fast-moving development; monthly or quarterly reviews help guide strategic focus.
During these cadences, apply a simple impact vs. effort score (1–5) to reevaluate priorities: a feature that scores high impact but low effort should be prioritized by the product team.
Step 3: Assign ownership and monitor progress
To keep everyone accountable, assign each goal to an owner or team, and monitor progress in Meegle.
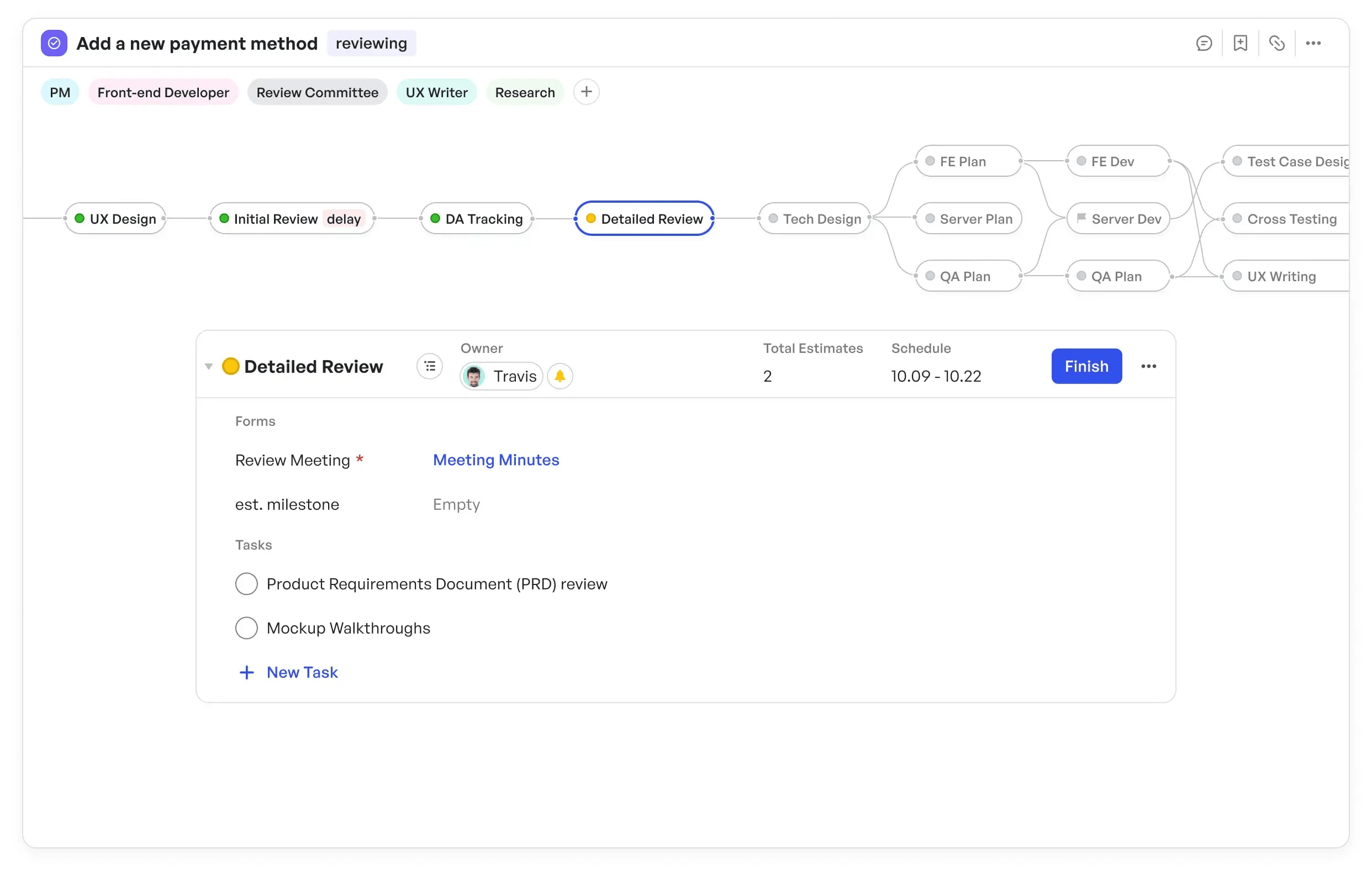 Assign owner and monitor progress in Meegle
Assign owner and monitor progress in MeegleStep 4: Keep your goals focused and current
To keep your goals effective, avoid setting vague metrics, taking on too many goals at once, or leaving plans unchecked for too long.
Finally, bring it all together using Meegle’s visual workflows and dashboards as your shared product tracking system.
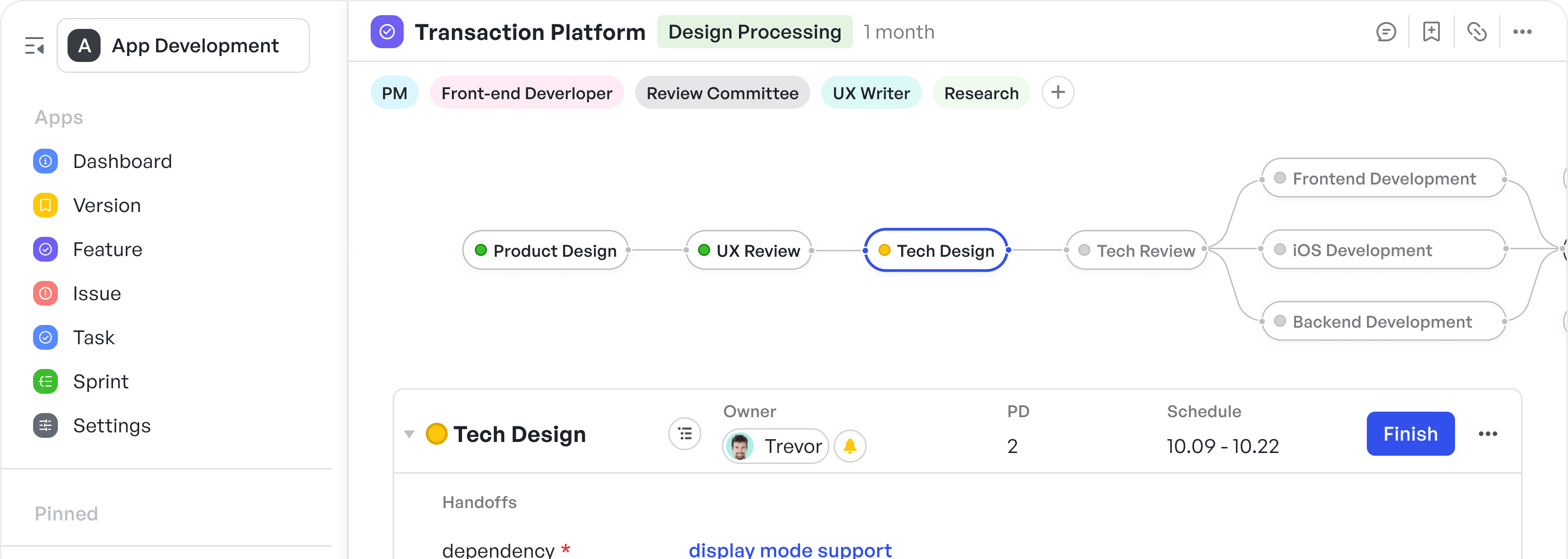
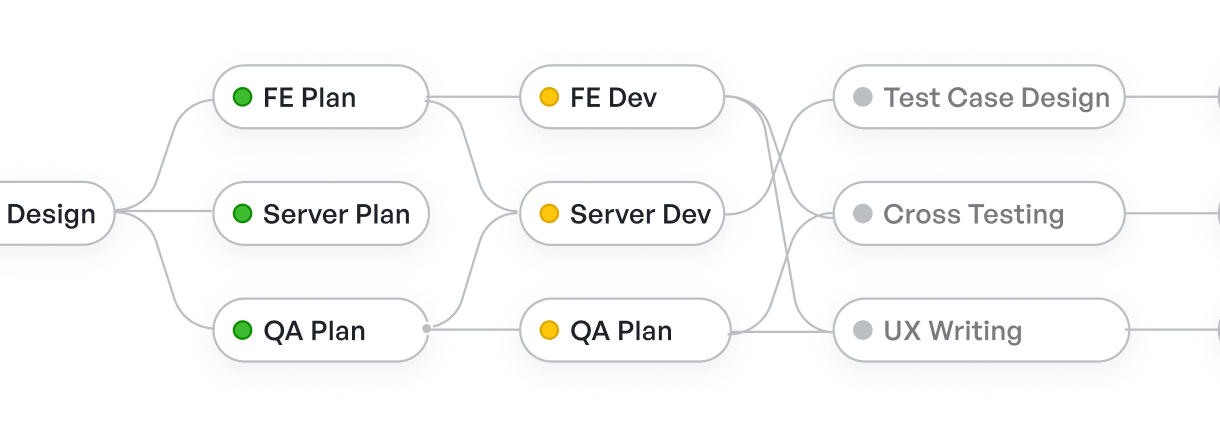 Track product manager goals with visual workflow
Track product manager goals with visual workflowYou can set deadlines and key metrics directly into each goal node. As your team updates status or moves dependencies, Meegle automatically reflects progress in real-time, reducing the need for manual follow-ups.
 Reduce manual follow ups, get real-time notification when team updates a status
Reduce manual follow ups, get real-time notification when team updates a statusSuggested Read:👉Step by Step Product Development Checklist for 2025
How Meegle supports product manager goals
When you're a newly hired product manager, there is a lot of uncertainty launching a new product. With limited time, a lean team, and pressure to hit the market fast, you'll need a clear system to plan, coordinate, and adapt.
To illustrate how Meegle can help, we'll use an example where you're the PM stepping into a startup building an AI-powered productivity tool designed to help remote teams manage focus, time, and priorities.
Suggested read: 👉What is Project Design? 7 Steps with Expert Tips [2025]
Visual workflows that align teams around shared objectives
The first challenge you'll likely face is aligning every team on what actually needs to be shipped.
Using Meegle’s visual workflows, you can outline a launch dashboard organized around key objectives: onboarding, core AI integrations, and user feedback. Each sprint is broken down into tasks with assigned owners, defined dependencies, and clear timelines.
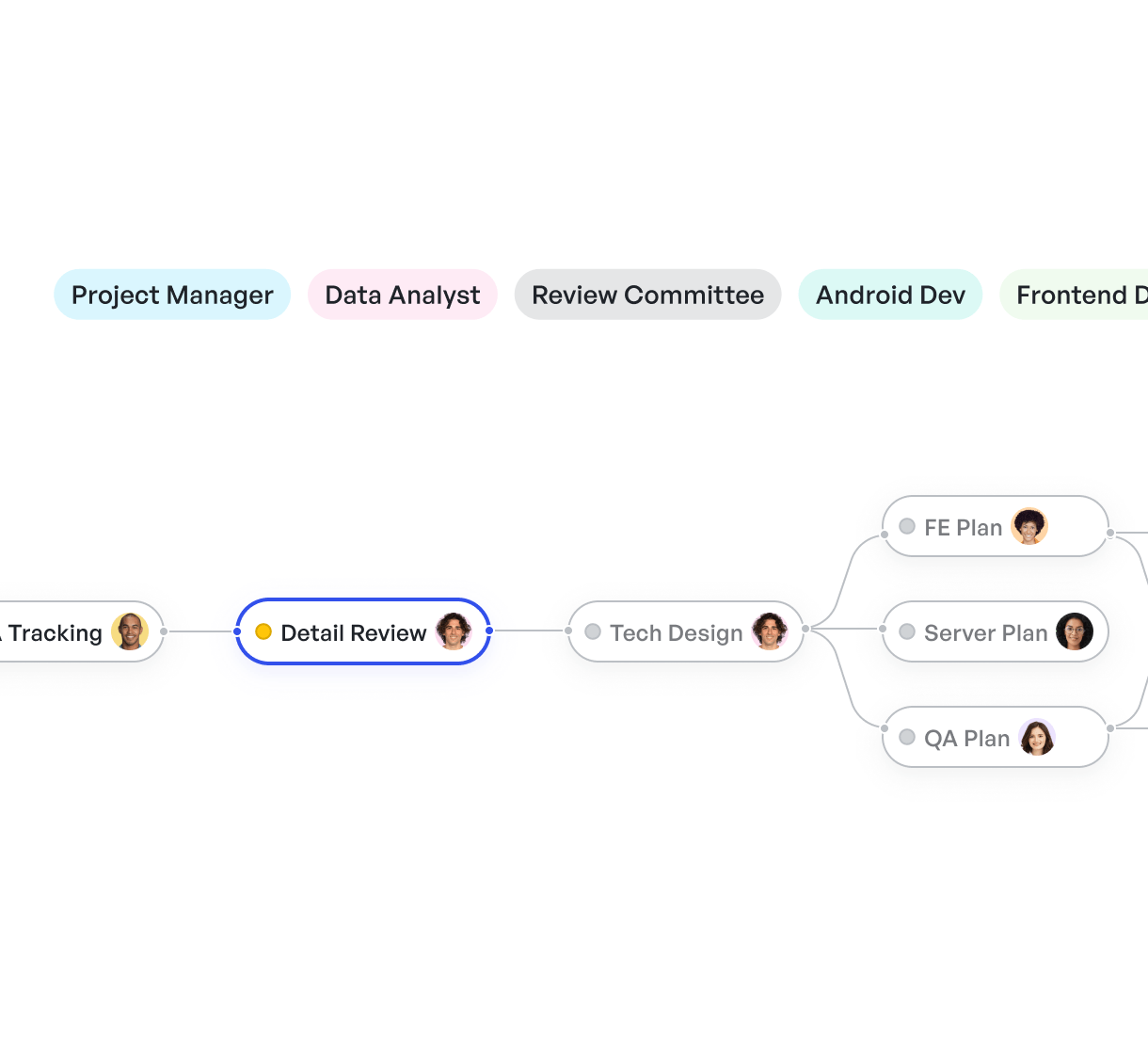 Visual dependencies helping hit your goals as a product manager
Visual dependencies helping hit your goals as a product managerSuggested read: 👉How to Write a Project Outline?
Meegle's node-driven workflow system allows you to map out tasks and processes, providing a visual representation that helps teams understand the sequence of activities and their interdependencies.
This ensures that everyone knows what to do and how it connects to the product’s goals, improving clarity and coordination across the team.
 Break down sprint with owners, dependencies and timelines
Break down sprint with owners, dependencies and timelinesReal-time progress tracking for product milestones
To keep dependencies on track, you can use Meegle’s milestone tracking features to define major checkpoints: first internal alpha, closed beta, public release.
 Track milestones with Meegle List View
Track milestones with Meegle List ViewThe List View automatically pulls progress data from linked tasks, updating milestone status in real time without manual input. That means the entire team can see what’s at risk or behind schedule at a glance.
Missed deadlines or blockers are flagged instantly with visual delay labels, helping you course-correct before they escalate into launch risks.
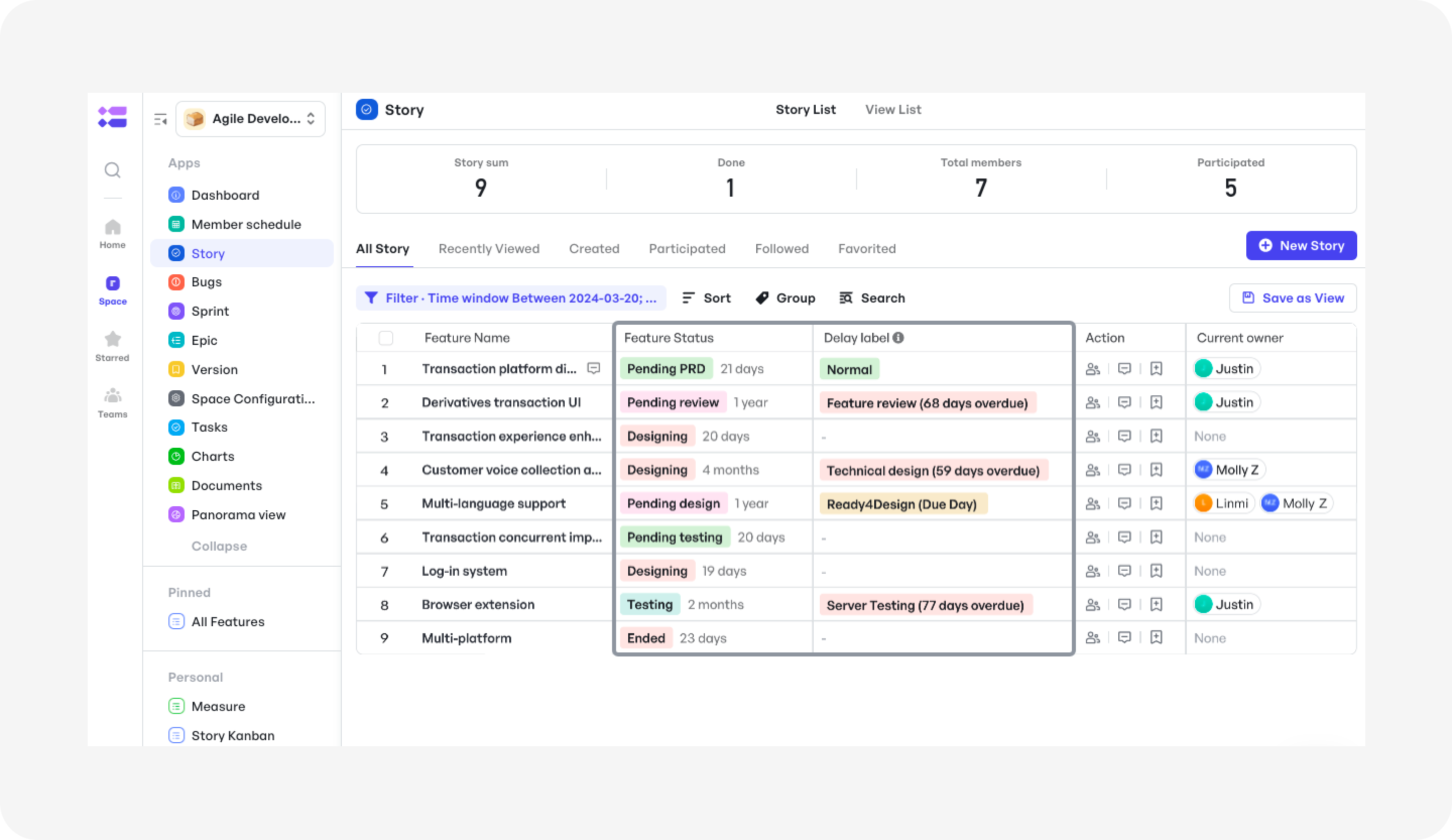 Spot delays with delay labels
Spot delays with delay labelsSuggested read: 👉7 best issue tracking software systems in 2025
Collaborative features that enhance cross-functional alignment
Meegle becomes your team’s shared space for cross-functional collaboration:
- Designers upload updated prototypes
- Engineers leave handoff notes
- Product marketing drafts launch messaging copy
Right inside the task nodes. Comments stay threaded under each task, and @mentions notify only the relevant people. Because every update lives next to work, there's no need to dig through Slack threads or bounce between tools to find feedback or decisions.
 Meegle inbox
Meegle inboxData-driven insights for informed decision making
Once beta testing begins, Meegle’s built-in analytics actively feed insights into your decision-making workflow. Each product usage pattern (like a feature being skipped or underused) is tied back to the task or objective it impacts.
 Analyse usage and engagement with Meegle’s analytics
Analyse usage and engagement with Meegle’s analyticsYou can define alert thresholds. For instance, if activation on a new feature drops below 40%, Meegle will flag the node in your roadmap. From there, you can instantly launch a follow-up experiment, assign new tasks, and link those to updated KPIs - all without leaving the dashboard.
 Updating visual workflow roadmap and documenting the reason
Updating visual workflow roadmap and documenting the reasonThis integrated feedback loop means decisions aren’t delayed by context-switching or manual analysis. Teams can respond faster, with clarity on why the shift happened and what they’re optimizing for.
Flexibility for adapting to changing priorities and goals
Like any product launch, things won’t always go as planned. You’ll deal with feature delays, new user feedback, or sudden changes from stakeholders.
Instead of starting over, use Meegle’s Views like Kanban or Gantt to revise timelines, reassign roles, and update your OKRs – all while keeping your broader objectives visible and intact.
When you shift a timeline in Gantt View, linked dependencies automatically adjust, and Meegle flags conflicts, like overlapping resource assignments or milestone delays, before they cause bottlenecks.
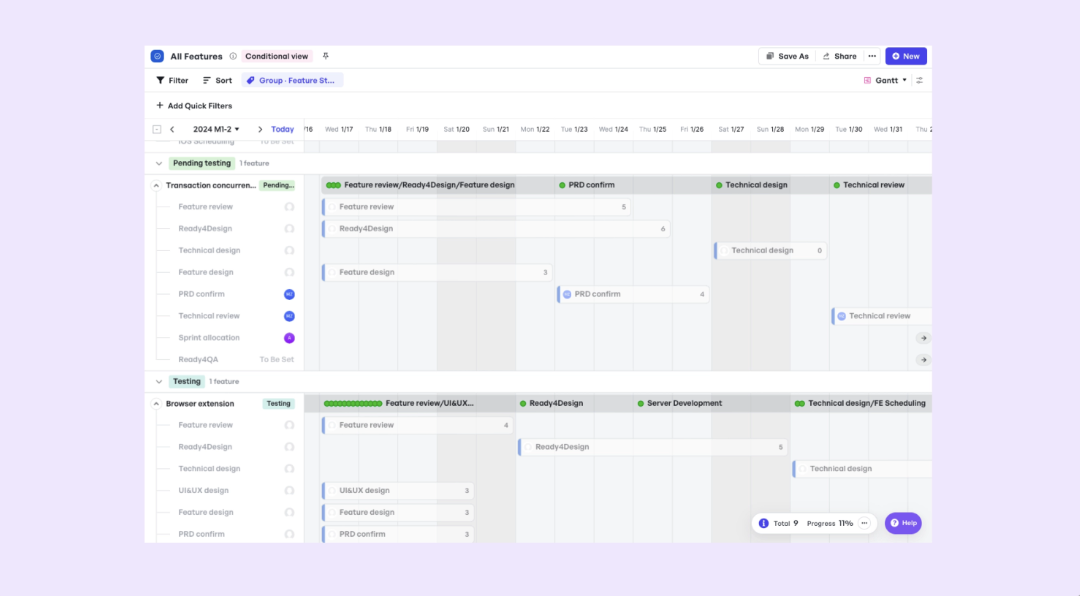 Revise timelines with Gantt View
Revise timelines with Gantt ViewYou can also define fallback roles: if a task owner is unavailable, Meegle automatically reassigns the task based on pre-set logic (e.g., next available team member by function or workload).
This reduces disruption during major changes and ensures accountability never drops.
For product managers launching new products (or new features), especially in complex spaces like AI, you'll need clarity, coordination, and adaptability.
Meegle brings structure, teamwork, and flexibility into a single product management system that helps teams stay focused on delivering outcomes rather than outputs.
Suggested Read:👉Product Management Dashboard: Types, Features & Benefits
Building your product manager goal roadmap for 2025
If there’s one thing you should learn from this guide, it’s that successful product managers plan with purpose.
In 2025, your goals should no longer focus on new features and timelines alone. They should focus on outcomes: creating real value for users and real results for the business. To build your own goal roadmap:
- Start with clarity: Choose one core objective that is important right now, like reducing churn or increasing activation, and stack 2–3 tactical goals beneath it.
- Make it measurable: Attach clear metrics to each goal (NPS, retention, TTV) so you know how to monitor progress.
- Keep it alive: Set regular check-ins. Use a 1–5 effort vs. impact scale when priorities compete. Revisit, revise, and refocus as your product evolves.
- Prioritize your business: Align each goal with your company’s overall strategy. Whether you’re driving growth, improving UX, or building trust, every decision should ladder up to a bigger outcome.
Your performance goals don’t have to be perfect. They just have to be visible, shared, and actionable. Meegle gives you the structure to do exactly that, with visual workflows, built-in analytics, and shared progress tracking that keeps teams aligned and moving forward.
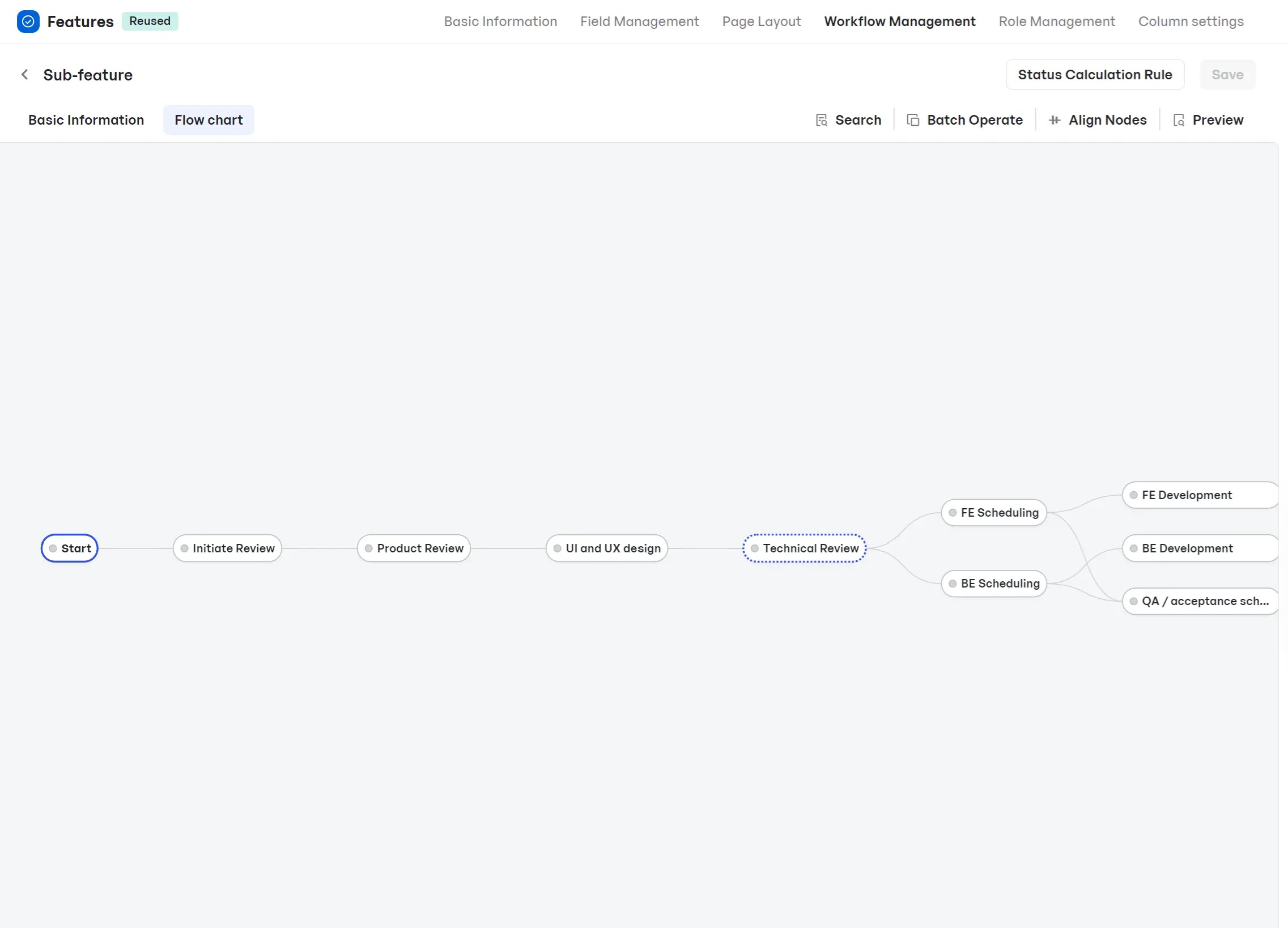 Visual workflow management
Visual workflow managementReady to crush your 2025 PM goals? Start achieving them with Meegle Today.
FAQs
What is the goal of a product manager?
A product manager’s goal is to turn vision into value by defining clear objectives that solve real user problems, drive measurable business outcomes (like retention and revenue), and keep cross-functional teams aligned toward shared success.
What are top 3 skills for a product manager?
1. Data-driven decision making: Using analytics and experiments to guide priorities.
2. Cross-functional leadership: Communicating and aligning engineering, design, and marketing.
3. Strategic prioritization: Framing goals that balance user needs, business impact, and effort.
What is a long term goal for a product manager?
A long-term goal is aligning your roadmap with broader business objectives, such as driving ARR growth or improving NPS over multiple quarters, ensuring every feature and initiative ladders up to sustained market fit and organizational strategy.
Which is the best tool for product managers in 2025?
Meegle stands out as the go-to platform for product managers, combining goal tracking, real-time collaboration, and roadmap alignment in one place to keep teams focused and outcomes measurable.
The world’s #1 visualized project management tool
Powered by the next gen visual workflow engineRead More
Check All BlogsStart creating impactful work today